Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "PDS Architecture"
(→Managed data service) |
(→HBX) |
||
| (139 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{#eclipseproject:technology.higgins|eclipse_custom_style.css}} [[Image:Higgins.funnell.PNG|right]] | + | {{#eclipseproject:technology.higgins|eclipse_custom_style.css}} [[Image:Higgins.funnell.PNG|right]] |
| − | + | This document describes the top level Higgins 2.0 PDS components under active development. Here are the bugzilla component names: | |
| + | * H2-Client | ||
| + | * H2-HBX | ||
| + | * H2-PDS | ||
| + | * H2-PDS Support | ||
| + | * H2-ADS | ||
| + | * H2-Data Model | ||
| − | == | + | == Front End == |
| − | + | There are two front end components: a web client, and a browser extension. | |
| − | + | [[Image:Higgins client 2.0.222.png|center]] | |
| − | + | === Client === | |
| − | + | The client is written in HTML and JavaScript and runs in any desktop browser (e.g. IE, FF, Safari, Chrome). In the future we also plan to make it display well on the limited screen size of smartphone mobile browser (e.g. iPhone, Android, etc.). | |
| − | + | * [[Org.eclipse.higgins.js.pds.client | .js.pds.client]] | |
| − | + | === HBX === | |
| − | + | The Higgins browser extension makes possible functionality like browser-side integration with other web APIs and sites, scraping and form filling. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | * .chrome.bx - Chrome-only Higgins Browser Extension | |
| − | * | + | * .js.pds.cde - Connection Data Engine 1. Loads CDE1-compatible JSON Scripts (See [[App-data vocabulary]]) from templates and uses them to implement auto-login, auto-registration, form filling, etc. |
| − | * | + | * [[org.eclipse.higgins.js.pds.cde2|.js.pds.cde2]] - Connection Data Engine 2. Loads CDE2-compatible JSON Scripts (See [[App-data vocabulary]]) from templates and uses them to implement auto-login, auto-registration, form filling, etc. |
| − | * | + | * .js.pds.connector.common |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | * | + | |
| − | === | + | ====Functionality==== |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | === | + | =====Browser interactions===== |
| + | When the user's browser lands on a new webpage it: | ||
| + | * Determines if the current PDS user is currently logged in. | ||
| + | ** This requires there be a template for the current site (domain) and that it contains an IsLoggedIn script | ||
| + | ** It is possible that a different PDS user (not the current PDS user) is currently logged in. | ||
| + | * If the user is not logged in then | ||
| + | ** It automatically logs the user in (or should it just auto-fill in the userid/password and wait for the user to click?) | ||
| + | * Looks for every appropriate form on the page | ||
| + | ** Automatically fills in each form as best it can -- this requires there be a template for the current site (domain) and that it contains a Fill script for this form (is there one fill script container with lots of per-form-submit-URL scripts? Or are there lots of Fill scripts each with an for-this-form-submit-URL attribute? | ||
| + | * Waits for the user to submit a form (including a login form with or without a custom template?) | ||
| + | ** Scrapes the form submit data and writes it into the PDS. If it is a login form then it writes into the proxy object, else the corresponding context | ||
| − | + | =====Web client interactions===== | |
| − | + | When the user opens a connection editor page (e.g. to edit the nytimes.com connection): | |
| − | + | * The BX immediately starts a background process to login and scrape the latest data values from the site. | |
| − | + | ** This is necessary because the user may have gone to the site directly (not using the PDS) and updated data values. A progress bar that shows this background process. | |
| + | * If the user edits an attribute it writes the updated attribute value to the site. | ||
| + | ** If this "write" operation happens before the background sync completes, there is some possibility for sync collisions and and confusion. | ||
| − | == | + | == Back End Components == |
| − | + | There are three back end components mostly written in Java and running in the cloud (e.g. Amazon AWS): | |
| − | + | *PDS | |
| + | *PDS Support | ||
| + | *ADS | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Higgins server 2.0.230.png|center]] | |
| − | + | ===PDS=== | |
| + | PDS Subcomponents: | ||
| − | + | *.pds.usermanager.ws - simple web service to manage user accounts, change password, etc. | |
| − | + | ===PDS Support=== | |
| + | PDS Support Subcomponents: | ||
| − | + | *.pds.client - wrapper around Open Anzo java client | |
| − | == | + | ===Attribute Data Storage=== |
| + | ADS Subcomponents: | ||
| − | * | + | *PLANNED: .ads.ld - Linked Data endpoint |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | == Data Model == | |
| − | Data | + | Data attributes whether created by the user or imported from an external service are stored in a common data model. This allows them to be consistently displayed to, and in some cases edited by, the user irrespective of its original source. We call this the [[Persona Data Model 2.0]]. |
| − | [[ | + | [[Category:Higgins 2]] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Latest revision as of 12:12, 4 January 2012
{{#eclipseproject:technology.higgins|eclipse_custom_style.css}}This document describes the top level Higgins 2.0 PDS components under active development. Here are the bugzilla component names:
- H2-Client
- H2-HBX
- H2-PDS
- H2-PDS Support
- H2-ADS
- H2-Data Model
Contents
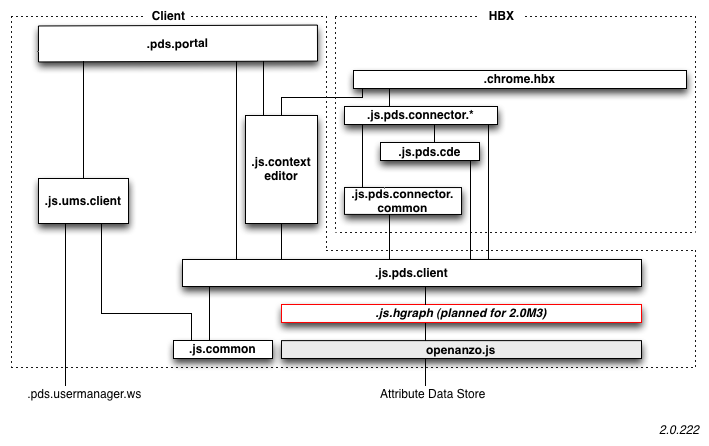
Front End
There are two front end components: a web client, and a browser extension.
Client
The client is written in HTML and JavaScript and runs in any desktop browser (e.g. IE, FF, Safari, Chrome). In the future we also plan to make it display well on the limited screen size of smartphone mobile browser (e.g. iPhone, Android, etc.).
HBX
The Higgins browser extension makes possible functionality like browser-side integration with other web APIs and sites, scraping and form filling.
- .chrome.bx - Chrome-only Higgins Browser Extension
- .js.pds.cde - Connection Data Engine 1. Loads CDE1-compatible JSON Scripts (See App-data vocabulary) from templates and uses them to implement auto-login, auto-registration, form filling, etc.
- .js.pds.cde2 - Connection Data Engine 2. Loads CDE2-compatible JSON Scripts (See App-data vocabulary) from templates and uses them to implement auto-login, auto-registration, form filling, etc.
- .js.pds.connector.common
Functionality
Browser interactions
When the user's browser lands on a new webpage it:
- Determines if the current PDS user is currently logged in.
- This requires there be a template for the current site (domain) and that it contains an IsLoggedIn script
- It is possible that a different PDS user (not the current PDS user) is currently logged in.
- If the user is not logged in then
- It automatically logs the user in (or should it just auto-fill in the userid/password and wait for the user to click?)
- Looks for every appropriate form on the page
- Automatically fills in each form as best it can -- this requires there be a template for the current site (domain) and that it contains a Fill script for this form (is there one fill script container with lots of per-form-submit-URL scripts? Or are there lots of Fill scripts each with an for-this-form-submit-URL attribute?
- Waits for the user to submit a form (including a login form with or without a custom template?)
- Scrapes the form submit data and writes it into the PDS. If it is a login form then it writes into the proxy object, else the corresponding context
Web client interactions
When the user opens a connection editor page (e.g. to edit the nytimes.com connection):
- The BX immediately starts a background process to login and scrape the latest data values from the site.
- This is necessary because the user may have gone to the site directly (not using the PDS) and updated data values. A progress bar that shows this background process.
- If the user edits an attribute it writes the updated attribute value to the site.
- If this "write" operation happens before the background sync completes, there is some possibility for sync collisions and and confusion.
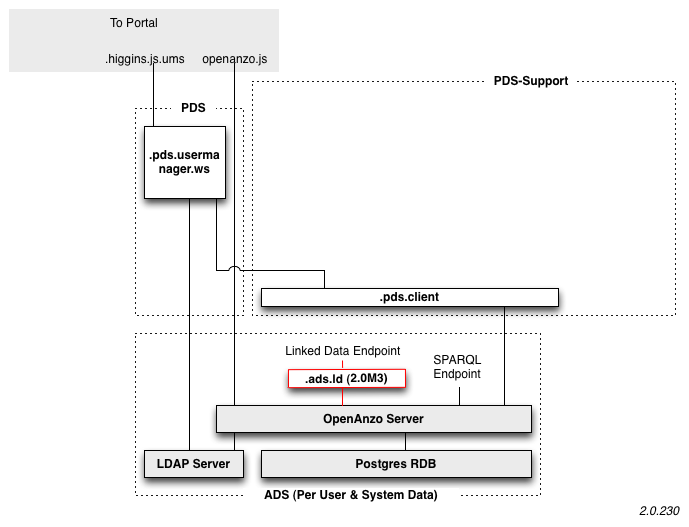
Back End Components
There are three back end components mostly written in Java and running in the cloud (e.g. Amazon AWS):
- PDS
- PDS Support
- ADS
PDS
PDS Subcomponents:
- .pds.usermanager.ws - simple web service to manage user accounts, change password, etc.
PDS Support
PDS Support Subcomponents:
- .pds.client - wrapper around Open Anzo java client
Attribute Data Storage
ADS Subcomponents:
- PLANNED: .ads.ld - Linked Data endpoint
Data Model
Data attributes whether created by the user or imported from an external service are stored in a common data model. This allows them to be consistently displayed to, and in some cases edited by, the user irrespective of its original source. We call this the Persona Data Model 2.0.