Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "EDT:Resource Binding Services"
(→Retrieving the binding detail and updating it in code) |
(→Defining a service binding in the EGL deployment descriptor) |
||
| (336 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | <span style="font-size:smaller;">< [[EDT:Resource Binding Introduction|Resource Binding Introduction]]</span> <br> | |
| − | + | <br> To access a service, you must specify both how to interact with the external logic and where it resides. You can think of the two kinds of information in an abbreviated way: "how" and "where."<br> | |
| − | + | = Specifying "how" and "where" in the call statement<br> = | |
| − | + | If you are accessing a service that was written in EGL, you can specify "how" and "where" in the '''call''' statement. <br><br>The usage is particularly simple and is available whether the service is being deployed with a Rich UI application (as a dedicated service) or outside of a Rich UI application (as an EGL REST-RPC service): <br> | |
| − | + | *The next example accesses either kind of service, depending on the EGL deployment-descriptor entry named <code>myEntry</code>: | |
| + | <pre>myBindingVar IHttp?{@Resource {uri="binding:myEntry"}}; | ||
| − | + | call | |
| + | MyServiceType.myFunction("abc") // "how" | ||
| + | using myBindingVar // "where" | ||
| + | returning to myCallBackFunction | ||
| + | onException myExceptionHandler; | ||
| + | |||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | :The example uses the <code>IHttp?</code> Interface type for flexibility. Later, if you want to switch to a different kind of access target, you switch to a different deployment descriptor. You will not need to change the invocation, and you will not need to regenerate the example. | ||
| − | = <br>Defining a service binding in the EGL deployment descriptor<br> = | + | *In the next example, the Service type identifies "how," and the lack of a '''call'''-statement '''using''' clause indicates that you are accessing a dedicated service: |
| + | <pre>call | ||
| + | MyServiceType.myFunction("abc") // "how" | ||
| + | // "where" (the service is deployed with the Rich UI application) | ||
| + | returning to myCallBackFunction | ||
| + | onException myExceptionHandler; | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | :This second case is even simpler, but any future use of an EGL REST-RPC service requires that you change the invocation and regenerate the example code. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Specifying "how" and "where" in a proxy function = | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you are accessing a REST or EGL REST-RPC service, you can encapsulate the "how" and "where" information in a single location, by adding a ''proxy function'' to a library or handler. The '''call''' statement invokes the proxy function, which acts as an intermediary between that statement and the backend code. You also specify a third kind of information in the proxy function, for use by the EGL generator that is storing invocation code in place of the annotations.<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | (The "proxy function" construct has been in use for some time for IBM i program access. The construct is now in use for service access, too. The change for service access occurred after EDT version .081 Milestone 2. For details on the prior support for service access, see the EDT help topics in the build for 0.81 Milestone 2.) | ||
| + | |||
| + | At development time, the proxy function is empty. It lists the invocation parameters and, if appropriate, a return type. Here is the outline of such a function: <br> | ||
| + | <pre>function myProxyFunction(p1 string, p2 string) RETURNS(int) | ||
| + | {} | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | You do not write any logic for the proxy function. Instead, you tell an EGL generator what is required. In particular, you specify an annotation that is specific to the kind of backend code that will be invoked. <br><br>Here are examples: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *If you are accessing a dedicated or EGL REST-RPC service, declare an '''EglService''' annotation:<br> | ||
| + | <pre>function myProxyFunction(p1 string, p2 string) RETURNS(int) { // "how" | ||
| + | @EglService{serviceName="MyServiceType"} // "what more" does the generator need? | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *If you are accessing a third-party REST service, declare a '''Rest''' annotation:<br> | ||
| + | <pre>function myProxyFunction02(p1 string, p2 string) RETURNS (int) { // "how" | ||
| + | @Rest // "what more" does the generator need? | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | method = HttpMethod._GET, | ||
| + | uriTemplate = "/org/search/?string01={p1}&string02={p2}" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | <br> To add "where" information to the proxy function, specify the '''Resource''' annotation at the same level as the other annotation. Here are the previous examples with the additional detail: | ||
| + | <pre>// for accessing a dedicated or EGL REST-RPC service | ||
| + | function myProxyFunction(p1 string, p2 string) RETURNS(int) { // "how" | ||
| + | @EglService{serviceName="MyServiceType"}, // "what more" | ||
| + | @Resource{uri = "binding:myEntry"} // "where" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | |||
| + | // for accessing a third-party REST service invocation | ||
| + | function myProxyFunction02(p1 string, p2 string) RETURNS(int) { // "how" | ||
| + | @Rest { // "what more" | ||
| + | method = HttpMethod._GET, | ||
| + | uriTemplate = "/org/search/?string01={p1}&string02={p2}" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | @Resource{uri = "binding:myEntry02"} // "where" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The '''Resource''' annotation in the proxy function is optional and, if present, is a default. The annotation is ignored if you specify the "where" detail in the code that invokes the proxy function. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Last, if the proxy function has a name different from the name of the service operation, declare an '''ExternalName''' annotation at the same level: | ||
| + | <pre>function myProxyFunction02(p1 string, p2 string) RETURNS(int) { // "how" | ||
| + | @Rest // "what more" | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | method = HttpMethod._GET, | ||
| + | uriTemplate = "/org/search/?string01={p1}&string02={p2}" | ||
| + | }, | ||
| + | @ExternalName{value = "my-Operation"}, // "what more" | ||
| + | @Resource{uri = "binding:myEntry02"} // "where" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | The primary reason to declare an '''ExternalName''' annotation is that the name of a third-party service operation is not valid as the name of an EGL proxy function.<br> <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Deciding on the placement of "how" and "where"<br> = | ||
| + | |||
| + | You say, "I can specify the 'how' and 'where' information in two places. What is the best practice?" | ||
| + | |||
| + | The proxy function is particularly useful when you are accessing a service that is in a more-or-less permanent location. In this case, you have the minor complexity of creating a proxy function, but you invoke the backend logic simply: | ||
| + | <pre>call | ||
| + | myProxyFunction("abc") // "how" and "where" | ||
| + | returning to myCallBackFunction | ||
| + | onException myExceptionHandler; | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | As shown, you have no binding variable and have hidden the "how" and "where" information in the proxy function. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you are coding a service written in EGL, you might avoid coding a proxy function at all. In this case, you rely on the Service type to tell "how." Two variations apply:<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *As shown earlier, the EGL deployer handles the "where" automatically if you are accessing a dedicated service. You can write a '''call''' statement without specifying either a binding variable or a '''call'''-statement '''using''' clause: | ||
| + | <pre>call | ||
| + | MyServiceType.myFunction("abc") // "how" | ||
| + | // "where" (the service is deployed with the Rich UI application) | ||
| + | returning to myCallBackFunction | ||
| + | onException myExceptionHandler; | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | *If you are developing an EGL REST-RPC service and want to switch easily between accessing the code being developed and, later, the code that is deployed, you can handle the situation by updating the deployment-descriptor entry or by switching deployment descriptors. The use of multiple deployment descriptors is robust, but requires that you assign the same-named entry in each of them.<!-- Alternatively, you can rely on the following rule: if the '''using''' clause is present but contains a null, a call to an EGL Service type accesses a dedicated service. Here is a partial example: | ||
| + | <pre>function callTheService() | ||
| + | |||
| + | try | ||
| + | myBindingVar IHttp? = Resources.getResource("binding:myEntry"); | ||
| + | onException(exception AnyException) | ||
| + | myBindingVar = null; | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | |||
| + | call | ||
| + | MyServiceType.myFunction() // "how" | ||
| + | using myBindingVar // "where" | ||
| + | returning to myCallBackFunction | ||
| + | onException myExceptionHandler; | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | |||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | If the EGL DD entry is present, the '''call''' statement accesses an EGL REST-RPC service. If the EGL DD entry is absent, the '''call''' statement accesses the service under development or, at run time, a dedicated service.<br> --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Specifying "where" in a service binding<br> = | ||
| + | |||
| + | A resource binding that is specifically for service access is known as a ''service binding''. The main detail in the EGL deployment descriptor is in one of three categories: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *If the service is deployed on an application server, you specify a Universal Resource Identifier (URI) that begins with the <code>http:</code> or <code>https:</code> prefix. Here is an example: | ||
| + | <pre>http://myserver:8080/myproject/restservices/myServiceType</pre> | ||
| + | :Although you can run the deployed service during an EGL debugging session, the EGL debugger does not step into the service.<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *If the Rich UI application accesses an EGL REST-RPC service, you can specify a ''workspace URI''. A workspace URI points to a workspace location, as shown here: | ||
| + | <pre>workspace://mySourceProject/servicepackage.myService</pre> | ||
| + | :The workspace URI is useful only at development time, and an internal Test Server enables you to debug the code. <br><br>In this case, your task in the EGL Deployment Descriptor editor is twofold: you update not only the Resource Binding tab, but the Service Deployment tab as well. That secondary requirement ensures that the deployment descriptor file includes the detail necessary to deploy the service. However, before you fulfill the EGL deployment step, you'll need to ensure that the URI in the resource binding is pointing to the deployed EGL REST-RPC service.<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *If a Rich UI application references a Service type in a way that indicates use of a dedicated service, an internal Test Server enables you to debug the service logic. The service binding, if any, has no detail.<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = <br>Defining a service binding in the EGL deployment descriptor<br> = | ||
| − | At this writing, you can bind to a REST | + | At this writing, you can bind to a REST, EGL REST-RPC, or dedicated service. The distinctions among the service types are explained here, with "binary-exchange service" in place of the more narrowly defined "dedicated service": [http://www.eclipse.org/edt/papers/topics/egl_soa_overview.html http://www.eclipse.org/edt/papers/topics/egl_soa_overview.html]. <br><br>To define a service binding for REST or EGL REST-RPC in the EGL deployment descriptor, do as follows: |
*In an EGL project, expand the EGLSource folder and double-click the deployment descriptor, which has the file extension '''.egldd'''. | *In an EGL project, expand the EGLSource folder and double-click the deployment descriptor, which has the file extension '''.egldd'''. | ||
*Click the Resource Bindings tab. The Resource Bindings Configuraton page is displayed. | *Click the Resource Bindings tab. The Resource Bindings Configuraton page is displayed. | ||
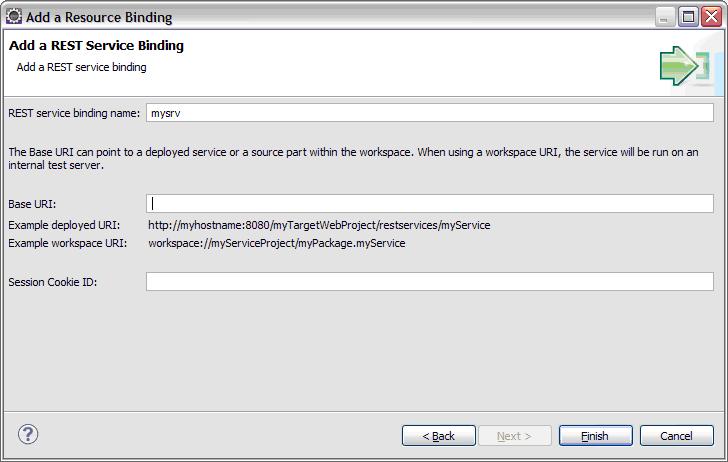
| − | *Click '''Add''' and select '''REST Service Binding'''. The Add a | + | *Click '''Add''' and, at the Add a Resource Binding page, select '''REST Service Binding'''. The Add a REST Service Binding page is displayed, as shown here:<br> |
| − | [[Image:Bind Img8.JPG]]<br> | + | [[Image:Bind Img8.JPG]]<br> |
| − | <br> | + | <br> |
| − | *In the topmost field, specify the binding name. You can reference that name in your code, whether in a '''Resource''' annotation or in a statement that invokes the ''' | + | *In the topmost field, specify the binding name. You can reference that name in your code, whether in a '''Resource''' annotation or in a statement that invokes the <span style="font-weight: bold;">Resources</span>'''.getResource '''function. |
*In the '''Base URI''' field, specify a URI, which might be a workspace URI: | *In the '''Base URI''' field, specify a URI, which might be a workspace URI: | ||
**If you are accessing an EGL REST-RPC service, specify the complete URI. | **If you are accessing an EGL REST-RPC service, specify the complete URI. | ||
| − | **If you are accessing a third-party REST service, you might decide to include only high-level details and to supplement them with values that are stored in | + | **If you are accessing a third-party REST service, you might decide to include only high-level details and to supplement them with values that are stored in a proxy function. If you include only high-level details, avoid placing extra spaces at the end of your input. |
*The '''sessionCookieID''' field is not in use. | *The '''sessionCookieID''' field is not in use. | ||
| − | + | If you are defining a service binding for a Service type in your workspace, you must ensure that the service will be deployed: | |
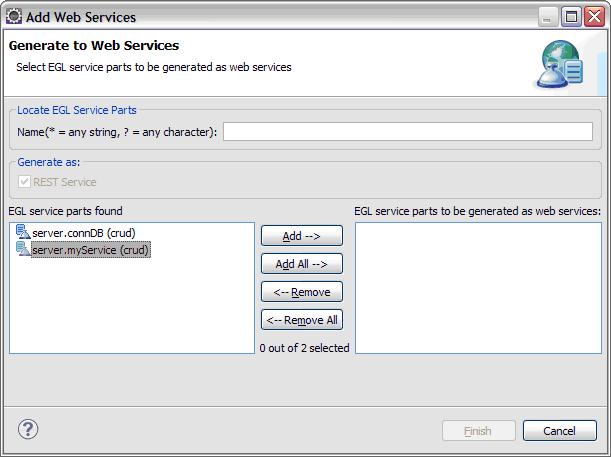
*Switch to the Service Deployment tab. If the service is not already listed, click '''Add'''. The '''Add Web Services''' page is displayed. | *Switch to the Service Deployment tab. If the service is not already listed, click '''Add'''. The '''Add Web Services''' page is displayed. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 176: | ||
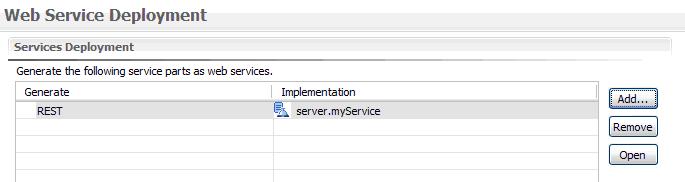
*Highlight the Service type of interest, click '''Add''', and click '''Finish'''. The Web Service Deployment tab is re-displayed with the new detail. | *Highlight the Service type of interest, click '''Add''', and click '''Finish'''. The Web Service Deployment tab is re-displayed with the new detail. | ||
| − | [[Image:Bind Img7.JPG]]<br> | + | [[Image:Bind Img7.JPG]]<br> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | *To save the deployment descriptor, press Ctrl-S.<br> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | < | + | |
| + | = Retrieving a service binding and changing it in your code<br> = | ||
| + | Here is an example of retrieving and changing a service binding and then using it to access a third-party REST service: | ||
| + | <pre>myBindingVariable IHttp? = Resources.getResource("binding:myEntry"); | ||
| + | myBindingVariable.request.encoding = encoding.json; | ||
| + | myBindingVariable.request.headers = new dictionary{edt.proxy.invocation.timeout = 6}; | ||
| + | |||
| + | call myProxyFunction() using myBindingVariable | ||
| + | returning to myCallBackFunction | ||
| + | onException myExceptionHandler; | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | <br>The code acts as follows: | ||
| + | #Declares a binding variable and creates an object that is based on the specified deployment-descriptor entry.<br><br> | ||
| + | #Adds detail to the object. In this example, the detail has two purposes: to ensure that data is transferred to and from the service in JSON format; and to establish a timeout value of 6 seconds.<br><br> | ||
| + | #Calls a proxy function, referencing the binding variable. The encoding detail takes precedence over the equivalent value, if any, in the proxy function. The headers detail can be set only in the code that invokes the proxy function.<br> | ||
| + | The example is accessing an instance of an HttpRest object. | ||
| − | + | = Creating a service binding in your code<br> = | |
| − | + | You can create a service binding in your code, in which case the EGL deployment descriptor is not involved. For example, you might substitute the first statement in the following code for the first three statements in the preceding section: | |
| − | + | <pre>myBindingVariable IHttp? = new HttpRest{ | |
| − | + | restType = eglx.rest.ServiceType.TrueRest, | |
| − | + | request.uri = "http://www.example.com/myproject/restservices/weather_service", | |
| + | request.encoding = Encoding.json, | ||
| + | request.headers = new dictionary{edt.proxy.invocation.timeout = 6}}; | ||
| − | + | call myProxyFunction() using myBindingVariable | |
| + | returning to myCallBackFunction | ||
| + | onException myExceptionHandler; | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | For details on the HttpRest object, see the help topic named "eglx.http package." | ||
| − | ♦ '''Next''': [ | + | <br>♦ '''Next''': [[EDT:Resource Binding Databases|SQL database bindings]] |
| − | ♦ '''Previous''': [ | + | ♦ '''Previous''': [[EDT:Resource Binding Introduction|Resource binding introduction]]<br> |
Latest revision as of 17:59, 7 September 2012
< Resource Binding Introduction
To access a service, you must specify both how to interact with the external logic and where it resides. You can think of the two kinds of information in an abbreviated way: "how" and "where."
Contents
- 1 Specifying "how" and "where" in the call statement
- 2 Specifying "how" and "where" in a proxy function
- 3 Deciding on the placement of "how" and "where"
- 4 Specifying "where" in a service binding
- 5 Defining a service binding in the EGL deployment descriptor
- 6 Retrieving a service binding and changing it in your code
- 7 Creating a service binding in your code
Specifying "how" and "where" in the call statement
If you are accessing a service that was written in EGL, you can specify "how" and "where" in the call statement.
The usage is particularly simple and is available whether the service is being deployed with a Rich UI application (as a dedicated service) or outside of a Rich UI application (as an EGL REST-RPC service):
- The next example accesses either kind of service, depending on the EGL deployment-descriptor entry named
myEntry:
myBindingVar IHttp?{@Resource {uri="binding:myEntry"}};
call
MyServiceType.myFunction("abc") // "how"
using myBindingVar // "where"
returning to myCallBackFunction
onException myExceptionHandler;
- The example uses the
IHttp?Interface type for flexibility. Later, if you want to switch to a different kind of access target, you switch to a different deployment descriptor. You will not need to change the invocation, and you will not need to regenerate the example.
- In the next example, the Service type identifies "how," and the lack of a call-statement using clause indicates that you are accessing a dedicated service:
call
MyServiceType.myFunction("abc") // "how"
// "where" (the service is deployed with the Rich UI application)
returning to myCallBackFunction
onException myExceptionHandler;
- This second case is even simpler, but any future use of an EGL REST-RPC service requires that you change the invocation and regenerate the example code.
Specifying "how" and "where" in a proxy function
If you are accessing a REST or EGL REST-RPC service, you can encapsulate the "how" and "where" information in a single location, by adding a proxy function to a library or handler. The call statement invokes the proxy function, which acts as an intermediary between that statement and the backend code. You also specify a third kind of information in the proxy function, for use by the EGL generator that is storing invocation code in place of the annotations.
(The "proxy function" construct has been in use for some time for IBM i program access. The construct is now in use for service access, too. The change for service access occurred after EDT version .081 Milestone 2. For details on the prior support for service access, see the EDT help topics in the build for 0.81 Milestone 2.)
At development time, the proxy function is empty. It lists the invocation parameters and, if appropriate, a return type. Here is the outline of such a function:
function myProxyFunction(p1 string, p2 string) RETURNS(int)
{}
end
You do not write any logic for the proxy function. Instead, you tell an EGL generator what is required. In particular, you specify an annotation that is specific to the kind of backend code that will be invoked.
Here are examples:
- If you are accessing a dedicated or EGL REST-RPC service, declare an EglService annotation:
function myProxyFunction(p1 string, p2 string) RETURNS(int) { // "how"
@EglService{serviceName="MyServiceType"} // "what more" does the generator need?
}
end
- If you are accessing a third-party REST service, declare a Rest annotation:
function myProxyFunction02(p1 string, p2 string) RETURNS (int) { // "how"
@Rest // "what more" does the generator need?
{
method = HttpMethod._GET,
uriTemplate = "/org/search/?string01={p1}&string02={p2}"
}
}
end
To add "where" information to the proxy function, specify the Resource annotation at the same level as the other annotation. Here are the previous examples with the additional detail:
// for accessing a dedicated or EGL REST-RPC service
function myProxyFunction(p1 string, p2 string) RETURNS(int) { // "how"
@EglService{serviceName="MyServiceType"}, // "what more"
@Resource{uri = "binding:myEntry"} // "where"
}
end
// for accessing a third-party REST service invocation
function myProxyFunction02(p1 string, p2 string) RETURNS(int) { // "how"
@Rest { // "what more"
method = HttpMethod._GET,
uriTemplate = "/org/search/?string01={p1}&string02={p2}"
},
@Resource{uri = "binding:myEntry02"} // "where"
}
end
The Resource annotation in the proxy function is optional and, if present, is a default. The annotation is ignored if you specify the "where" detail in the code that invokes the proxy function.
Last, if the proxy function has a name different from the name of the service operation, declare an ExternalName annotation at the same level:
function myProxyFunction02(p1 string, p2 string) RETURNS(int) { // "how"
@Rest // "what more"
{
method = HttpMethod._GET,
uriTemplate = "/org/search/?string01={p1}&string02={p2}"
},
@ExternalName{value = "my-Operation"}, // "what more"
@Resource{uri = "binding:myEntry02"} // "where"
}
end
The primary reason to declare an ExternalName annotation is that the name of a third-party service operation is not valid as the name of an EGL proxy function.
Deciding on the placement of "how" and "where"
You say, "I can specify the 'how' and 'where' information in two places. What is the best practice?"
The proxy function is particularly useful when you are accessing a service that is in a more-or-less permanent location. In this case, you have the minor complexity of creating a proxy function, but you invoke the backend logic simply:
call
myProxyFunction("abc") // "how" and "where"
returning to myCallBackFunction
onException myExceptionHandler;
As shown, you have no binding variable and have hidden the "how" and "where" information in the proxy function.
If you are coding a service written in EGL, you might avoid coding a proxy function at all. In this case, you rely on the Service type to tell "how." Two variations apply:
- As shown earlier, the EGL deployer handles the "where" automatically if you are accessing a dedicated service. You can write a call statement without specifying either a binding variable or a call-statement using clause:
call
MyServiceType.myFunction("abc") // "how"
// "where" (the service is deployed with the Rich UI application)
returning to myCallBackFunction
onException myExceptionHandler;
- If you are developing an EGL REST-RPC service and want to switch easily between accessing the code being developed and, later, the code that is deployed, you can handle the situation by updating the deployment-descriptor entry or by switching deployment descriptors. The use of multiple deployment descriptors is robust, but requires that you assign the same-named entry in each of them.
Specifying "where" in a service binding
A resource binding that is specifically for service access is known as a service binding. The main detail in the EGL deployment descriptor is in one of three categories:
- If the service is deployed on an application server, you specify a Universal Resource Identifier (URI) that begins with the
http:orhttps:prefix. Here is an example:
http://myserver:8080/myproject/restservices/myServiceType
- Although you can run the deployed service during an EGL debugging session, the EGL debugger does not step into the service.
- If the Rich UI application accesses an EGL REST-RPC service, you can specify a workspace URI. A workspace URI points to a workspace location, as shown here:
workspace://mySourceProject/servicepackage.myService
- The workspace URI is useful only at development time, and an internal Test Server enables you to debug the code.
In this case, your task in the EGL Deployment Descriptor editor is twofold: you update not only the Resource Binding tab, but the Service Deployment tab as well. That secondary requirement ensures that the deployment descriptor file includes the detail necessary to deploy the service. However, before you fulfill the EGL deployment step, you'll need to ensure that the URI in the resource binding is pointing to the deployed EGL REST-RPC service.
- If a Rich UI application references a Service type in a way that indicates use of a dedicated service, an internal Test Server enables you to debug the service logic. The service binding, if any, has no detail.
Defining a service binding in the EGL deployment descriptor
At this writing, you can bind to a REST, EGL REST-RPC, or dedicated service. The distinctions among the service types are explained here, with "binary-exchange service" in place of the more narrowly defined "dedicated service": http://www.eclipse.org/edt/papers/topics/egl_soa_overview.html.
To define a service binding for REST or EGL REST-RPC in the EGL deployment descriptor, do as follows:
- In an EGL project, expand the EGLSource folder and double-click the deployment descriptor, which has the file extension .egldd.
- Click the Resource Bindings tab. The Resource Bindings Configuraton page is displayed.
- Click Add and, at the Add a Resource Binding page, select REST Service Binding. The Add a REST Service Binding page is displayed, as shown here:
- In the topmost field, specify the binding name. You can reference that name in your code, whether in a Resource annotation or in a statement that invokes the Resources.getResource function.
- In the Base URI field, specify a URI, which might be a workspace URI:
- If you are accessing an EGL REST-RPC service, specify the complete URI.
- If you are accessing a third-party REST service, you might decide to include only high-level details and to supplement them with values that are stored in a proxy function. If you include only high-level details, avoid placing extra spaces at the end of your input.
- The sessionCookieID field is not in use.
If you are defining a service binding for a Service type in your workspace, you must ensure that the service will be deployed:
- Switch to the Service Deployment tab. If the service is not already listed, click Add. The Add Web Services page is displayed.
- Highlight the Service type of interest, click Add, and click Finish. The Web Service Deployment tab is re-displayed with the new detail.
- To save the deployment descriptor, press Ctrl-S.
Retrieving a service binding and changing it in your code
Here is an example of retrieving and changing a service binding and then using it to access a third-party REST service:
myBindingVariable IHttp? = Resources.getResource("binding:myEntry");
myBindingVariable.request.encoding = encoding.json;
myBindingVariable.request.headers = new dictionary{edt.proxy.invocation.timeout = 6};
call myProxyFunction() using myBindingVariable
returning to myCallBackFunction
onException myExceptionHandler;
end
The code acts as follows:
- Declares a binding variable and creates an object that is based on the specified deployment-descriptor entry.
- Adds detail to the object. In this example, the detail has two purposes: to ensure that data is transferred to and from the service in JSON format; and to establish a timeout value of 6 seconds.
- Calls a proxy function, referencing the binding variable. The encoding detail takes precedence over the equivalent value, if any, in the proxy function. The headers detail can be set only in the code that invokes the proxy function.
The example is accessing an instance of an HttpRest object.
Creating a service binding in your code
You can create a service binding in your code, in which case the EGL deployment descriptor is not involved. For example, you might substitute the first statement in the following code for the first three statements in the preceding section:
myBindingVariable IHttp? = new HttpRest{
restType = eglx.rest.ServiceType.TrueRest,
request.uri = "http://www.example.com/myproject/restservices/weather_service",
request.encoding = Encoding.json,
request.headers = new dictionary{edt.proxy.invocation.timeout = 6}};
call myProxyFunction() using myBindingVariable
returning to myCallBackFunction
onException myExceptionHandler;
end
For details on the HttpRest object, see the help topic named "eglx.http package."
♦ Next: SQL database bindings
♦ Previous: Resource binding introduction