Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "Java17/Examples"
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
|Code fails to compile with below error:<br> | |Code fails to compile with below error:<br> | ||
String cannot be resolved to a variable | String cannot be resolved to a variable | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Negative compilation3 (Pattern Matching for switch Example) | ||
| + | | Use the following code: | ||
| + | <source lang="java"> | ||
| + | public class X { | ||
| + | private static void foo(Object o) { | ||
| + | switch (o.hashCode()) { | ||
| + | case Integer t: | ||
| + | default : System.out.println("Object"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | public static void main(String[] args) { | ||
| + | foo("Hello World"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }</source> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[File:Pattern-matching-switch-negative4-Java17.png]] | ||
| + | |Code fails to compile with below error:<br> | ||
| + | Type mismatch: cannot convert from int to Integer | ||
|- | |- | ||
! colspan="3" | Standard Feature: Sealed Classes | ! colspan="3" | Standard Feature: Sealed Classes | ||
Revision as of 07:08, 25 August 2021
This is an informal page listing examples of features that are implemented by the Java 17 Support, which can be installed from the Marketplace. You are welcome to try out these examples. If you find bugs, please file a bug after checking for a duplicate entry here
Watch out for additional examples being added soon.
NOTE:
- Sealed Classes is standard features in Java 17.
- Restore Always-Strict Floating-Point Semantics is a standard features in Java 17.
- Pattern Matching for switch is preview feature in Java 17. They are not enabled by default and can by enabled using --enable-preview.
- In Eclipse, --enable-preview can be enabled from the Preferences. It is implicitly added while launching a java program if the feature has been enabled for the project/workspace.
| Feature / Steps | Expected Result | |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Java/JRE setup with Eclipse | More details can be found on dedicated Java/JRE setup page. | Setting up Java/JRE in Eclipse. |
| Overview of eclipse.ini | More details can be found on dedicated eclipse.ini page. | Specifying the JVM in eclipse.ini |
| Preview Feature: Pattern Matching for switch | ||
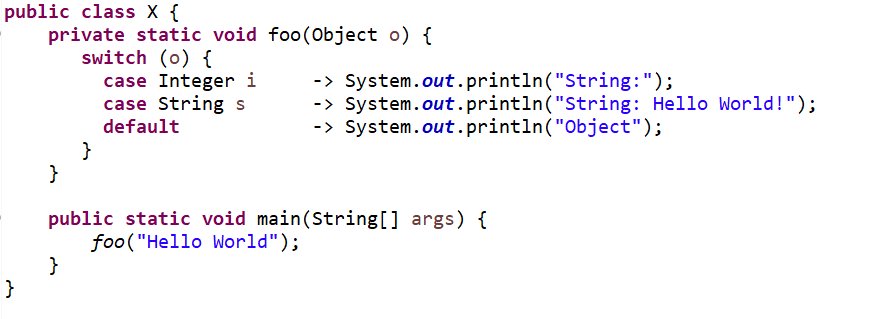
| Postive compilation1 (Pattern Matching for switch Example) | Use the following code:
public class X { private static void foo(Object o) { switch (o) { case Integer i -> System.out.println("String:"); case String s -> System.out.println("String: Hello World!"); default -> System.out.println("Object"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { foo("Hello World"); } } |
Code compiles and prints below message String: Hello World! |
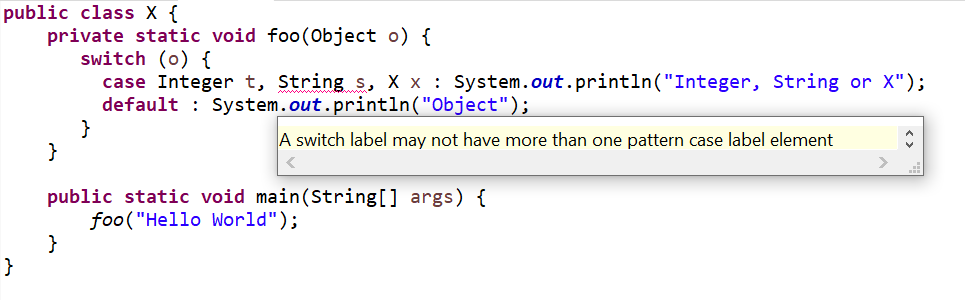
| Negative compilation1 (Pattern Matching for switch Example) | Use the following code:
public class X { private static void foo(Object o) { switch (o) { case Integer t, String s, X x : System.out.println("Integer, String or X"); default : System.out.println("Object"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { foo("Hello World"); } } |
Code fails to compile with below error: A switch label may not have more than one pattern case label element |
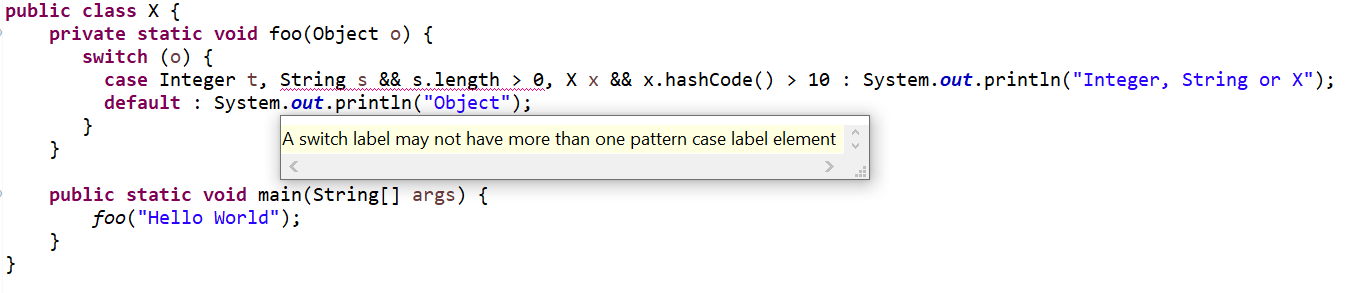
| Negative compilation2 (Pattern Matching for switch Example) | Use the following code:
public class X { private static void foo(Object o) { switch (o) { case Integer t, String s && s.length > 0, X x && x.hashCode() > 10 : System.out.println("Integer, String or X"); default : System.out.println("Object"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { foo("Hello World"); } } |
Code fails to compile with below error: A switch label may not have more than one pattern case label element |
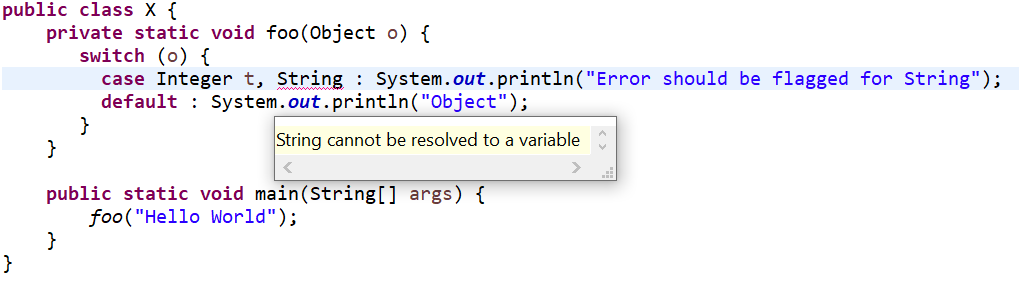
| Negative compilation3 (Pattern Matching for switch Example) | Use the following code:
public class X { private static void foo(Object o) { switch (o) { case Integer t, String : System.out.println("Error should be flagged for String"); default : System.out.println("Object"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { foo("Hello World"); } } |
Code fails to compile with below error: String cannot be resolved to a variable |
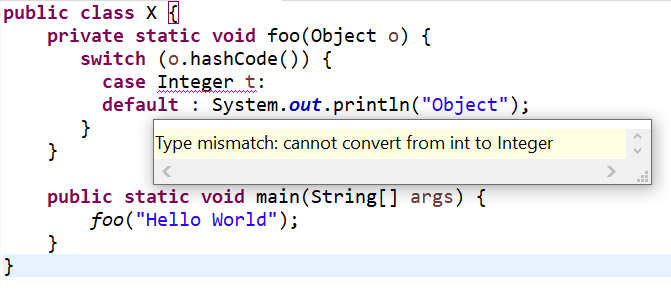
| Negative compilation3 (Pattern Matching for switch Example) | Use the following code:
public class X { private static void foo(Object o) { switch (o.hashCode()) { case Integer t: default : System.out.println("Object"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { foo("Hello World"); } } |
Code fails to compile with below error: Type mismatch: cannot convert from int to Integer |
| Standard Feature: Sealed Classes | ||
| Postive compilation1 (Sealed Class Example) | Use the following code:
sealed class Y permits X { } non-sealed class X extends Y { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(0); } } |
Code compiles and prints 0. |
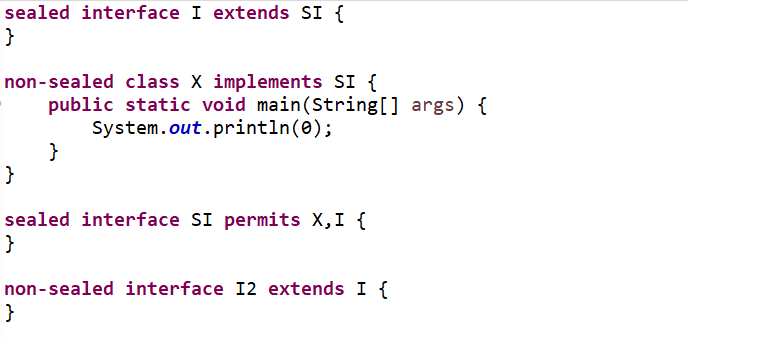
| Postive compilation2 (Sealed Class Example) | Use the following code:
sealed interface I extends SI { } non-sealed class X implements SI { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(0); } } sealed interface SI permits X,I { } non-sealed interface I2 extends I { } |
Code compiles and prints 0. |
| Postive compilation3 (Sealed Class Example) | Use the following code:
sealed class X permits Y { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(100); } } non-sealed class Y extends X { } |
Code compiles and prints 100. |
| Postive compilation4 (Sealed Class Example) | Use the following code:
sealed public class X<T> { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(100); } } non-sealed class Y extends X { } |
Code compiles and prints 100. |
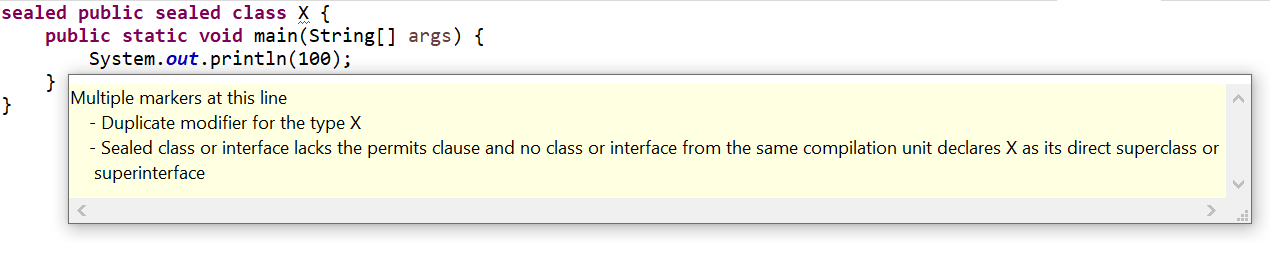
| Negative compilation1 (Sealed Class Example) | Use the following code:
sealed public sealed class X { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(100); } } |
Code fails to compile with error "Multiple markers at this line
- Duplicate modifier for the type X - Sealed class or interface lacks the permits clause and no class or interface from the same compilation unit declares X as its direct superclass or superinterface" |
| Syntax coloring for “sealed”, “non-sealed”, “permits” | New restricted keywords are colored | |
| "Match locations" dialog supports "Permitted type declarations" | "Search > Java Search > Match locations" dialog supports "Permitted type declarations" check-box option. | |