Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
EclipseLink/UserGuide/DBWS/Overview
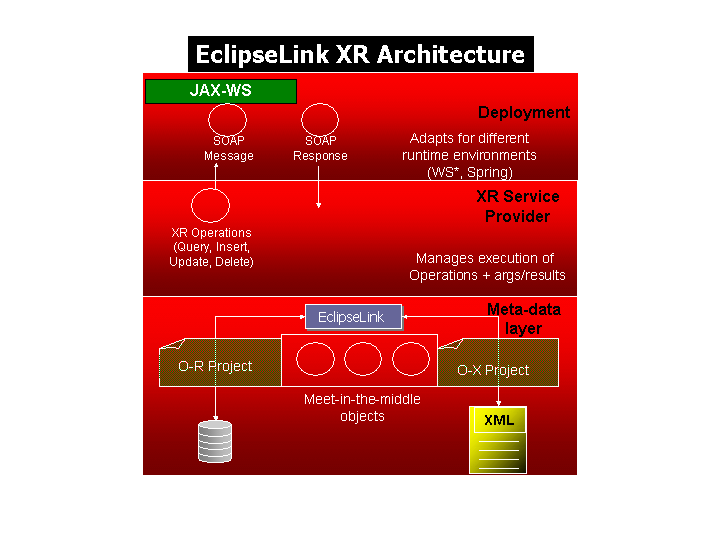
EclipseLink DBWS Overview
The goal of EclipseLink DBWS is to enable simple and efficient access to relational database artifacts via a Web service, extending EclipseLink's core capabilities while leveraging existing components (ORM, OXM).
EclipseLink DBWS has two parts: a design-time tooling component (DBWSBuilder) and a runtime provider component that takes a service descriptor (along with related deployment artifacts) and realizes it as a JAX-WS 2.0 Web service. The runtime provider uses EclipseLink to bridge between the database and the XML SOAP Messages used by Web service clients.
An EclipseLink DBWS service may be comprised of any number of operations of which there are 4 types:
- Insert - inserts into the database persistent entities described by an XML document.
- Update - updates database persistent entities described by an XML document.
- Delete - removes from the database persistent entities described by an XML document.
- Query - retrieves from the database persistent entities described by an XML document.
Selection criteria for Query operations can be specified by:- custom SQL
- Stored Procedures
- EclipseLink Named Queries (can use the complete range of EclipseLink ORM Expression Framework APIs)
The XML documents used by an operation conform to an XML Schema Definition (.xsd file) auto-generated by the design-time tooling. Alternatively, if no .xsd is available, a pre-defined simple XML format (SXF) is used.
Concept: XML-to-Relational Mapping (XRM)
EclipseLink's ORM and OXM features provides the basis for a powerful bridge between a database's relational structure(s) and XML's hierarchical structure.
Configuration
The metadata for an EclipseLink DBWS service is contained in an easy-to-read service descriptor file eclipselink-dbws.xml:
- contains name of EclipseLink DBWS service
- contains name of sessions.xml - if not present, then eclipselink-dbws-sessions.xml will be used
- operation definitions
- contains eclipselink-dbws-schema.xsd XML Schema Definition file
Example DBWS Service descriptor file
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <dbws xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" > <name>example</name> <query> <name>countEmployees <result> <type>xsd:int</type> </result> <sql><![CDATA[select count(*) from EMP]]></sql> </query> </dbws>
The information required by the EclipseLink DBWS service descriptor file is kept to a minimum and omitted fields have simple defaults, allowing for both auto-generation by tools or manual editing.
XML Schema Definition
An EclipseLink DBWS service requires an XML Schema Definition file to specify how information returned from the database is to be shaped. The EclipseLink OXM Project handles converting information from the database to XML, giving the user access to the complete range of EclipseLink Object-to-XML mapping capabilities.
An example of an auto-generated XML Schema
The design-time tool derives element-tag names from Database table metadata (column names, types, nullable, etc):
| OWNER | TABLE_NAME | COLUMN_NAME | DATA_TYPE | DATA_LENGTH | DATA_PRECISION | DATA_SCALE | NULLABLE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCOTT | EMP | EMPNO | NUMBER | 22 | 4 | 0 | N |
| SCOTT | EMP | ENAME | VARCHAR2 | 10 | (null) | (null) | Y |
| SCOTT | EMP | JOB | VARCHAR2 | 9 | (null) | (null) | Y |
| SCOTT | EMP | MGR | NUMBER | 22 | 4 | 0 | Y |
| SCOTT | EMP | HIREDATE | DATE | 7 | (null) | (null) | Y |
| SCOTT | EMP | SAL | NUMBER | 22 | 7 | 2 | Y |
| SCOTT | EMP | COMM | NUMBER | 22 | 7 | 2 | Y |
| SCOTT | EMP | DEPTNO | NUMBER | 22 | 2 | 0 | Y |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <xsd:schema xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" > <xsd:complexType name="empType"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="empno" type="xsd:int" xsi:nil="false"/> <xsd:element name="ename" type="xsd:string" xsi:nil="true"/> <xsd:element name="job" type="xsd:string" xsi:nil="true"/> <xsd:element name="mgr" type="xsd:int" minOccurs="0" xsi:nil="true"/> <xsd:element name="hiredate" type="xsd:dateTime" xsi:nil="true"/> <xsd:element name="sal" type="xsd:decimal" xsi:nil="true"/> <xsd:element name="comm" type="xsd:int" minOccurs="0" xsi:nil="true"/> <xsd:element name="deptno" type="xsd:int" xsi:nil="true"/> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType> <xsd:element name="emp" type="empType"/> </xsd:schema>
If no schema can be generated or none is provided by the user, a pre-defined Simple XML Format (SXF) can be used.
SXF uses information only available at the time of query execution to build the XML element-tag names; thus, these XML documents cannot be validated against any schema.
