Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
EDT:Resource Binding Services
If the purpose of a resource binding is service access, the definition is called a service binding, and the main detail is in one of three formats:
- If the service is deployed on an application server, you can specify a Universal Resource Identifier (URI). The URI begins with the
http:orhttps:prefix (not shown) and continues with a string like this one://myserver:8080/myproject/restservices/myService
- Although you can run the deployed service during an EGL debugging session, the EGL debugger does not step into the service.
- If the service is available in your workspace and was written in EGL, you can use a workspace URI, which is an identifier that points to a workspace location. Here is an example:
workspace://mySourceProject/servicepackage.myService
- In this case, the URI is useful only at development time, and an internal Test Server enables you to debug the code.
- If a Rich UI application includes a Service type that will be deployed as a dedicated service, an Internal Test Server enables you to debug the code. In this case, the EGL deployment descriptor is never used. The only binding detail is the DedicatedService annotation, which is part of the service-access variable declaration.
If a Service part namedMyServiceTypeis a dedicated service, the declaration might be as follows:myService MyServiceType {@DedicatedService}
Contents
Defining a service binding in the EGL deployment descriptor
Binding service @Resource
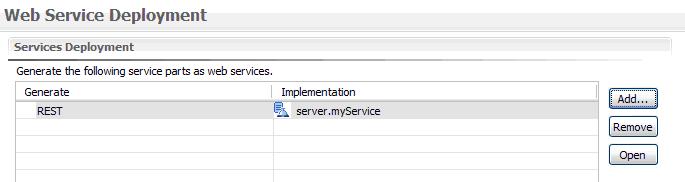
In order to binding the service via @Resource, you should add the service into the Services Deployment.
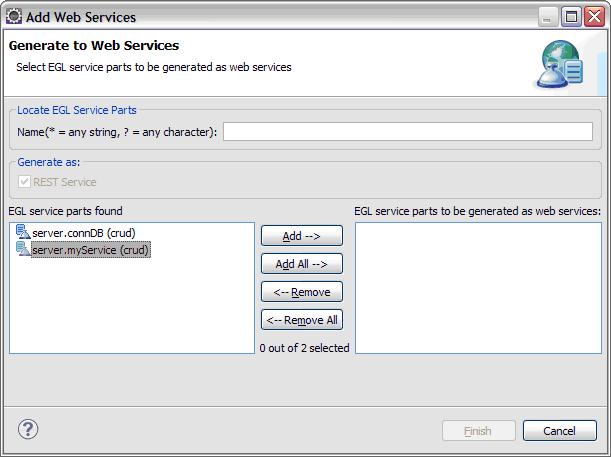
Open the egldd file and switch to “Service Deployment” tab. Then click the Add button.
You can add the service myService into your Services Deployment setting up.
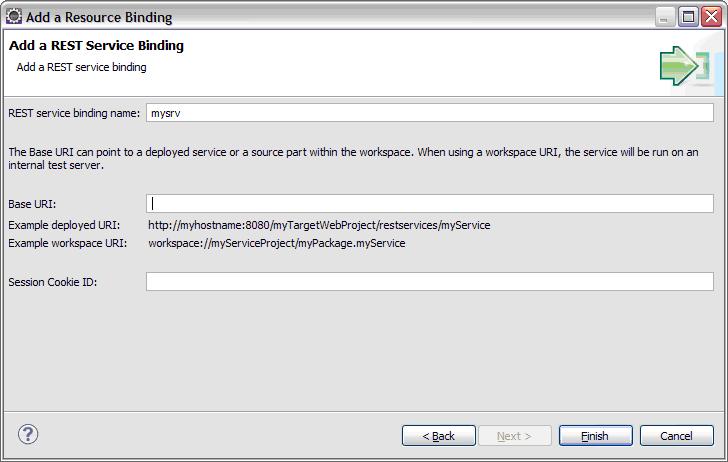
Then switch to Resource Bindings tab to add the REST service binding. Click Add button and select “Rest Service Binding” to add the service binding.
You should give a name for your service binding. For the Base URI you can use two types of URI as the instruction in the dialog.
- Deployed URI.
Myhostname:8080 is your project server’s host and port number.
“myTargetWebProject” is the project name which you want to deploy into. You can find the name in “Overview” tab of the elgdd file
“restservices”. Fixed string. Please do NOT modify it
“myService” : your service’s name.
- Workspace URI
“myServiceProject” : your project’s name.
“myPackage.myservice”: your service’s name and its project’s name
Click Finish to complete the binding.
Use the service binding in code
In source code you can use the service binding your defined in section 3.1 as below:
mysrv mysrv ?{@Resource {}};
mysrv mysrv?{ @Resource { propertyFileName = “egldd file name” , bindingkey = “ REST service name”}}
Then you can call the methods in myService
♦ Next: Database bindings
♦ Previous: Resource binding introduction
[[Category: EDT]]