Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Editing Derived Ids in JPA Diagram Editor
Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 Derived Ids
- 3 Configuring Derived Identifiers
- 3.1 The parent entity has a simple primary key and the dependent entity has a single primary key attribute which is mapped by the relationship attribute.
- 3.2 The parent entity has a simple primary key and the dependent entity has a single primary key attribute corresponding to the relationship attribute. The primary key attribute is of the same basic type as the primary key of the parent entity.
- 3.3 The parent entity has a simple primary key and the dependent entity uses IdClass to represent a composite key.
- 3.4 The parent entity has a simple primary key and the dependent entity uses EmbeddedId to represent a composite key.
- 3.5 The parent entity has a composite primary key (IdClass) and the dependent entity uses IdClass to represent a composite key.
- 3.6 The parent entity has a composite primary key (IdClass) and the dependent entity uses EmbeddedId to represent a composite key.
Overview
Every entity must have a primary key. The primary key must be defined on the entity class that is the root of the entity hierarchy or on a mapped superclass that is a (direct or indirect) superclass of all entity classes in the entity hierarchy. The primary key must be defined exactly once in an entity hierarchy.
Derived Ids
The identity of an entity may be derived from the identity of another entity (the "parent" entity) when the former entity (the "dependent" entity) is the owner of a many-to-one or one-to-one relationship to the parent entity and a foreign key maps the relationship from dependent to parent.
In palette of the JPA diagram editor, there shall be a new section, named Derived Identifiers, which shall contain two palette entry: One-to-One and Many-to-One:
Configuring Derived Identifiers
The identifier in either of the entities might be composed of one or a plurality of attributes. The relationship from the dependent entity to the parent entity might make up the entire derived identifier, or there might be additional state in the dependent entity that contributes to it. One of the entities might have a simple or compound primary key, and in the compound case might have an id class or an embedded id class. All of these factors combine to produce a multitude of scenarios, each of which requires slightly different configurations.
The parent entity has a simple primary key and the dependent entity has a single primary key attribute which is mapped by the relationship attribute.
The source code shall look like this:
@Entity public class Person { @Id String ssn; } @Entity public class MedicalHistory { // default join column name is overridden @Id @OneToOne @JoinColumn(name="FK") Person patient; }
In the JPA editor it means that there shall be an entity Person with primary key ssn and an entity MedicalHistory without any primary keys. When the One-to-One uni-directional relation feature is selected from the Derived Identifiers palette, the connection which will be created shall have as owner the MedicalHistory entity and as target the Person entity. When the new connection is created, a new attribute patient shall be added in the MedicalHistory entity and shall be mapped as primary key:
The parent entity has a simple primary key and the dependent entity has a single primary key attribute corresponding to the relationship attribute. The primary key attribute is of the same basic type as the primary key of the parent entity.
The source code shall look like this:
@Entity public class Person { @Id String ssn; } @Entity public class MedicalHistory { @Id String id; // overriding not allowed // default join column name is overridden @MapsId @JoinColumn(name="FK") @OneToOne Person patient; }
In the JPA editor it means that there shall be an entity Person with primary key ssn and an entity MedicalHistory with primary key id. When the One-to-One uni-directional relation feature is selected from the Derived Identifiers palette, the connection which will be created shall have as owner the MedicalHistory entity and as target the Person entity. When the new connection is created, a new attribute patient shall be added in the MedicalHistory entity and shall be mapped as primary key:
The parent entity has a simple primary key and the dependent entity uses IdClass to represent a composite key.
The source code shall look like this:
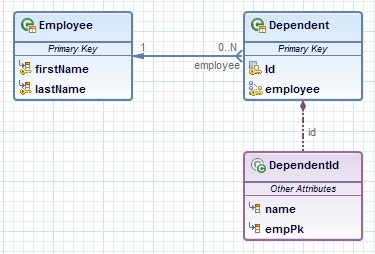
@Entity public class Employee { @Id long id; String empName; } public class DependentId { String name; // matches name of @Id attribute long emp; // matches name of @Id attribute and type of Employee PK } @Entity @IdClass(DependentId.class) public class Dependent { @Id String name; // id attribute mapped by join column default @Id @ManyToOne Employee emp; }
In the JPA editor it means that there shall be an entity Employee with primary key id and an entity Dependent with composite primary key name. When the Many-to-One uni-directional relation feature is selected from the Derived Identifiers palette, the connection which will be created shall have as owner the Dependent entity and as target the Employee entity. During the creation of the connection it shall be checked if the Dependent entity has a composite primary key (IdClass) and if this IdClass contains an attribute of the same type as the type of the primary key of the Employee entity. If such an attribute is missing it shall be added authomatically. When the new connection is created, a new attribute with the same name as the attribute in the IdClass shall be added in the Dependent entity and shall be mapped as primary key:
The parent entity has a simple primary key and the dependent entity uses EmbeddedId to represent a composite key.
The source code shall look like this:
@Entity public class Employee { @Id long id; String empName; } public class DependentId { String name; long empPK; // corresponds to PK type of Employee } @Entity public class Dependent { @EmbeddedId DependentId id; // id attribute mapped by join column default @MapsId("empPK") // maps empPK attribute of embedded id @ManyToOne Employee emp; }
In the JPA editor it means that there shall be an entity Employee with primary key id, an embeddable DependentId and an entity Dependent that uses the emebeddable as EmbeddedId. When the Many-to-One uni-directional relation feature is selected from the Derived Identifiers palette, the connection which will be created shall have as owner the Dependent entity and as target the Employee entity. During the creation of the connection it shall be checked if the Dependent entity has a composite primary key (EmbeddedId) and if this embeddable class contains an attribute of the same type as the type of the primary key of the Employee entity. If such an attribute is missing it shall be added authomatically. When the new connection is created, a new attribute of of the parent entity shall be added in the Dependent entity and shall be mapped as id by the parent entity's attribute in the embeddable class:
The parent entity has a composite primary key (IdClass) and the dependent entity uses IdClass to represent a composite key.
The source code shall look like this:
public class EmployeeId { String firstName; String lastName; } @Entity @IdClass(EmployeeId.class) public class Employee { @Id String firstName @Id String lastName } public class DependentId { String name; // matches name of attribute EmployeeId emp; //matches name of attribute and type of Employee PK } @Entity @IdClass(DependentId.class) public class Dependent { @Id String name; @Id @JoinColumns({ @JoinColumn(name="Employee_firstName", referencedColumnName="firstName"), @JoinColumn(name="Employee_lastName", referencedColumnName="lastName") }) @ManyToOne Employee emp; }
In the JPA editor it means that there shall be an entity Employee with composite primary key (IdClass) that has two fields firstName and lastNameand an entity Dependentwith composite primary key name. When the Many-to-One uni-directional relation feature is selected from the Derived Identifiers palette, the connection which will be created shall have as owner the Dependent entity and as target the Employee entity. During the creation of the connection it shall be checked if the Dependent entity has a composite primary key (IdClass) and if this IdClass contains an attribute of the same type as the type of the composite primary key of the Employee entity (the same type as the IdClass). If such an attribute is missing it shall be added authomatically. When the new connection is created, a new attribute with the same name as the attribute in the IdClass shall be added in the Dependent entity, the columns of the parent entity shall be obtained and shall be automatically mapped with the JoinColumns annotation. The newly created attribute shall be mapped as primary key:
The parent entity has a composite primary key (IdClass) and the dependent entity uses EmbeddedId to represent a composite key.
The source code shall look like this:
public class EmployeeId { String firstName; String lastName; } @Entity @IdClass(EmployeeId.class) public class Employee { @Id String firstName @Id String lastName } public class DependentId { String name; // matches name of attribute EmployeeId empPK; //matches name of attribute and type of Employee PK } @Entity public class Dependent { @EmbeddedId DependentId id; @MapsId("empPK") @JoinColumns({ @JoinColumn(name="Employee_firstName", referencedColumnName="firstName"), @JoinColumn(name="Employee_lastName", referencedColumnName="lastName") }) @ManyToOne Employee emp; }
In the JPA editor it means that there shall be an entity Employee with composite primary key (IdClass) that has two fields firstName and lastName, an embeddable DependentId and an entity Dependent that uses the emebeddable as EmbeddedId. When the Many-to-One uni-directional relation feature is selected from the Derived Identifiers palette, the connection which will be created shall have as owner the Dependent entity and as target the Employee entity. During the creation of the connection it shall be checked if the Dependent entity has a composite primary key (EmbeddedId) and if this embeddable class contains an attribute of the same type as the type of the composite primary key of the Employee entity (the same type as the parent's IdClass). If such an attribute is missing it shall be added authomatically. When the new connection is created, a new attribute of the parent entity shall be added in the Dependent entity, the columns of the parent entity shall be obtained and shall be automatically mapped with the JoinColumns annotation. The newly created attribute shall be mapped as id by the parent entity's attribute in the embeddable class: