Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
CosmosDataReportingComponent10
Back to Data Reporting Design
Contents
Overview
As the architecture of COSMOS becomes more defined tooling is required to facilitate the adoption of the COSMOS platform and components.
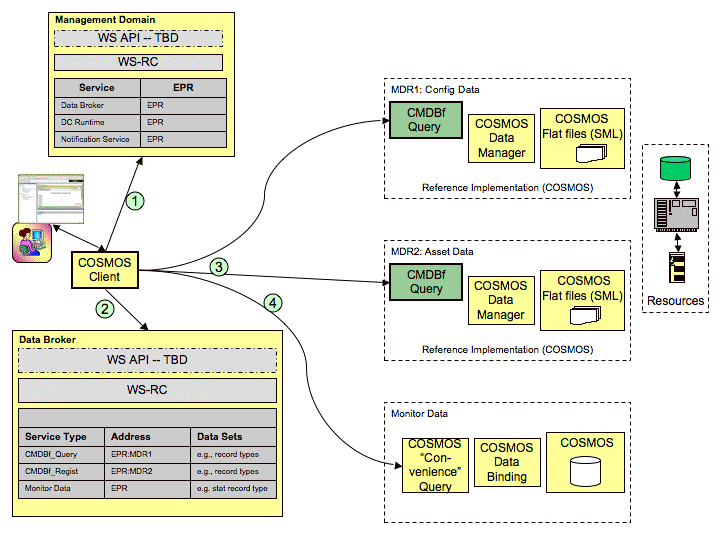
One of the main the focus of the data visualization sub project is to provide reusable user interface components to help facilitate the development and validation of Management Data Repositories (MDRs) as defined by the Configuration Management Database Specification Federation specification (CMDBf). An MDR is a CMDBf term that represents a component that contains data about managed resources (e.g. computer systems, application software and building) and/or process artifacts (e.g. incident records and requests for change forms) and the relationships between them. Consider the following high level architecture of the COSMOS platform.
The COSMOS project will not be providing a federating CMDB, but rather the building blocks that can be used in a federated scenario. One of these building blocks, and a key component of the COSMOS platform, is the data broker. The data broker is a middleware component that provides a means to lookup a set of management data repositories (MDRs). Adopters of the COSMOS platform will provide a set of MDRs to access their systems. The data broker may be used by a federating CMDB to lookup the endpoints of the MDRs that have registered with it. Another part of the COSMOS platform is the management domain. The management domain provides the necessary bootstrapping that provides the client with an entry point into the COSMOS runtime. The management domain provides a registry mechanism for the data brokers.
From the perspective of COSMOS, it is only necessary to provide an initial view to visualize the contents of the management domain. Specifically, a user interface is required to show the list of brokers that are registered with the management domain. Consider the following mockup that shows the various views involved in the COSMOS UI. Note each view is highlighted in red.
- The Navigator view will initially show the contents of the management domain in a tree structure. The top level nodes will show a list of brokers registered with the management domain. The second level of the tree will show the list of MDRs registered for each broker.
- The properties view shows a collapsable table that shows properties on a particular tree node. For example, when a user clicks on an MDR the properties view will show the known properties such as the classification, query service the MDR supports and the EPR adddress.
- The details page will show a visualization that knows how to render the contents of the MDR that is selected.
Note: it is expected that the same type of content will be offered by multiple MDRs, for example, more than one management system provides configuration information. As the way content is represented becomes standardized, e.g. SML, the views that render the content will become part of the building blocks offered by COSMOS. Common data representation and the decoupling of views from the MDRs facilitates the rapid customization and specialization of the COSMOS user interface.
The COSMOS User interface is a web interface that is based on a framework that uses Web 2.0 concepts. These concepts are outlined in the data visualization design document [[1]].
Design
At the very basic level the views in COSMOS are constructed from a set of web gadgets building blocks. These gadgets are very simple so that they can be reused to construct different user interface views. For example, the COSMOS user interface provides a gadget that visualizes a tree. An "event wiring point" is defined at each tree node that allows an event to be triggered and published to a communication bus. One possible function of this wiring point is to trigger the repaint event of another widget. Each gadget has a corresponding data feed that is served by a REST service. Consider the following diagram.
Note the current implementation of each REST service provides a JSON data feed. The structure of the JSON data is consumed by a JavaScript class that visualizes the tree. Note that the JSON data structure provides a contract between the backend data and the user interface. This architecture provides a clear decoupling between the raw data and the user interface. As a result, new UI widgets that conform to the JSON contract can be constructed to create different visualizations.
The COSMOS user interface framework provides a set of extension mechanisms:
- Widgets - A set of widgets can be registered to a specific UI tag. This allows for custom widgets to visualize custom data.
- View layouts - the layout of the views are defined by an XML file
- Styles - cosmetic styles are defined in style sheets
- Data Feeds - data feeds can be associated with a particular widget to produce different visualizations
- Report templates - reports templates are constructed using the BIRT framework
The following sections define the COSMOS user interface views. Each section is then broken down further to define the gadgets and data feeds needed.
Managment Domain Widget
A widget is required to visualize the contents of the data broker. This view will be composed of a tree widget that will show a list of brokers registed with the management domain. Under each broker a list of associated MDRs are shown.
Mockup
Published Events
- Select - When the user clicks on a node within the tree the widget publishes a 'Select' event to the event bus that contains the node id. This will notify any widget listening to the event bus that a node was clicked with a particular id.
Subscribed Events
- None
Widgets
- Tree View - this widgets consumes a JSON data feed that contains a list of MDRs organized by classification. The widget shows the MDR names in the tree node. When the user clicks on a tree node an event is thrown to the properties widget with the MDR id.
- Properties Table - this widget listens to the event bus for an event that contains a MDR id. The id is then sent to a REST service that provides the meta data for the MDR. An action button is rendered that sends an event with the MDR id to the parent widget to visualize the custom MDR UI.
Data Feeds
- Managed Domain feed - Provides a JSON feed that contains the list of brokers that are registered with the Domain. Note the JSON feed should conform to a tree data structure. The following shows a JSON feed that lists 3 brokers. The first broker contains 3 MDRs while the other two brokers have 1 MDR each.
{ identifier: "object", label: "title",
items:[
{nodeClass:"broker",title:"Broker 1",object:"9106612", children:[{reference:"13064916"},{reference:"1845558"},reference:"14005505"}]},
{nodeClass:"broker",title:"Broker 2",object:"9106613", children:[{reference:"55064916"}]},
{nodeClass:"broker",title:"Broker 3",object:"9106614", children:[{reference:"14043505"}]},
{nodeClass:"mdr",title:"MDR1",object:"1845558"},
{nodeClass:"mdr",title:"MDR2",object:"13064916"},
{nodeClass:"mdr",title:"MDR3",object:"14005505"},
{nodeClass:"mdr",title:"MDR4",object:"55064916"},
{nodeClass:"mdr",title:"MDR5",object:"14043505"},
]
}
SML Repository View
This is a custom view that understands how to visualize an MDR that represents a SML repository. This view is composed of a tree view and a properties view.
Widgets
- Tree View - visualizes a set of SML resources and facets. The widget shows the SML resource names as tree nodes. When the user clicks on a tree node an event is thrown to the properties widget with the resource id.
- Properties Table - this widget listens to the event bus for an event that contains a resource id. The id is then sent to a REST service that provides the properties for the SML resource
Data Feeds
These feeds will use CMDBf to query the SML repository and construct the JSON feed. - SML resource list - provides a JSON feed that contains the list of resources. Note the JSON feed should conform to a tree data structure. - Resource properties - provides a JSON feed that contains a list of properties for a particular resource. Note the JSON feed should conform to a table data structure.
Statistical/CBE View
This is a custom view that will present the user with a list of data sources and a properties view. The view will also allow the user to generate a report on a particular data source. For example, consider an MDR that contains statistical data for several tomcat servers and operating systems. This view will list all the set of tomcat servers and operating servers as data sources contain statistical data. The user has the option to click on a particular data source. At this point a properties table displays the meta data information for the data source (e.g. data source name, type of data collected, etc.). In addition a drop down button is provided that shows a set of available statistical reports that can be used to visualize the data collected.
Widgets
- List View - visualizes a set of data sources. The widget shows the data source names as list nodes. When the user clicks on a node an event is thrown to the properties widget with the data source id.
- Properties Table - this widget listens to the event bus for an event that contains a data source id. The id is then sent to a REST service that provides the properties for the data source.
- Available Report Button - a drop down button that shows the available reports that can be used to visualize the data. When the user selects a particular report an event is sent to the BIRT report viewer widget.
- BIRT report viewer - This sends a request to the BIRT reporting system to render the report given the data source id and report template id.
Data Feeds
These feeds will use CMDBf to query the SML repository and construct the JSON feed.
- SML resource list - provides a JSON feed that contains the list of resources. Note the JSON feed should conform to a tree data structure.
- Resource properties - provides a JSON feed that contains a list of properties for a particular resource. Note the JSON feed should conform to a table data structure.
- Available report list - provides a JSON feed that contains a list of report template names and ids that can be used for a particular data type (i.e. statistical, CBE).
CMDBf Query Builder
This is a generic view that provides a user interface to allow the end user to submit CMDBf queries to an MDR that supports CMDBf queries. This view is composed of a widget that allows the user to construct a CMDBf query and submit the query to a REST service. A results view will render the graph response to the screen.
Widgets
- Query builder - initially this widget will be a simple text box that the user can freely construct a CMDBf query with a submit button. The submit action will trigger an event which is sent to the graph response widget along with the construct red query.
- Graph response - this widget will visualize the graph response as plain text.
Data Feeds
- Graph response - this data feed takes in a CMDBf query and returns the XML graph response.
Glossary
- JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) [2] is a light-weight interchange format. It is used as the interchange format because the Javascript widgets can easily serialize and deserialize Java objects over the network.