Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "BaSyx / Documentation / API / ControlComponentProfiles"
(Moved profile sections from BaSyx_/_Documentation_/_API_/_ControlComponent) |
m (Rearranged common profile values.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | <!-- BaSys 4.2 Deliverable D-3.2 and D-4.6--> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <!-- BaSys 4.2 Deliverable D-4.6 --> | + | |
{{warning|1= | {{warning|1= | ||
This information is work in progress as part of the ''BaSys 4.2'' project. This section is preliminary and subject to change during the project. | This information is work in progress as part of the ''BaSys 4.2'' project. This section is preliminary and subject to change during the project. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| − | + | | [[BaSyx_/_Documentation_/_ControlComponentProfiles | Overview]] <nowiki>|</nowiki> [[BaSyx_/_Documentation_/_API_/_ControlComponentProfiles | Interface]] <nowiki>|</nowiki> [[BaSyx_/_Documentation_/_Implementation_/_ControlComponentProfiles | Implementation]] | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | <!-- TODO | + | <!--TODO describe this page in short--> |
| − | == | + | == Profiles == |
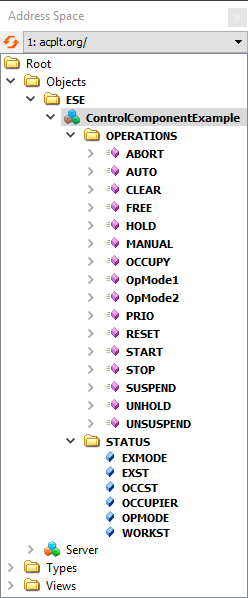
[[File:BaSyx-ControlComponent-Example-OPCUA-SI5-OC4-EM3-ES3-OM4.png|thumb|An example control component in OPC UA with the following profile: SI=5, OC=4, EM=3, ES=3, OM=4]] | [[File:BaSyx-ControlComponent-Example-OPCUA-SI5-OC4-EM3-ES3-OM4.png|thumb|An example control component in OPC UA with the following profile: SI=5, OC=4, EM=3, ES=3, OM=4]] | ||
| Line 48: | Line 29: | ||
: Describes whether multiple [[BaSyx_/_Documentation_/_API_/_ControlComponent#Operation mode state machine|operation modes]] are available and need to be selcted. | : Describes whether multiple [[BaSyx_/_Documentation_/_API_/_ControlComponent#Operation mode state machine|operation modes]] are available and need to be selcted. | ||
: Variants may describe whether there are specific operation modes, like fallback or startup and shutdown modes. | : Variants may describe whether there are specific operation modes, like fallback or startup and shutdown modes. | ||
| − | |||
For example a control component could have the following profile values. | For example a control component could have the following profile values. | ||
| Line 59: | Line 39: | ||
<!-- TODO add more examples --> | <!-- TODO add more examples --> | ||
<!-- TODO maybe move examples to "Implementation" page? --> | <!-- TODO maybe move examples to "Implementation" page? --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Profile Values == | ||
| + | |||
| + | All profiles shall be determined with an positiv integer or zero, respectively enums may be implemented. | ||
| + | In order to combine profile values and to use them as statements some common values are equal for all profiles, which is presented in the following table. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | ! Value !! Name !! Description | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 0 || UNKNOWN || No statement about profile or not determined | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1 || NONE || Profile is not realised, used, compliant or implemented | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2 || ANY || One ore more profile values, but not specified which ones | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 3 - n || Profile specific || Specific variants of the profile. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <!-- TODO define a way how profile values can be concenated, as bitmask for example. --> | ||
=== SI Profile === | === SI Profile === | ||
| Line 84: | Line 82: | ||
| 0 - 2 | | 0 - 2 | ||
| UNKNOWN, NONE, ANY | | UNKNOWN, NONE, ANY | ||
| − | | See [[# | + | | See [[#Profile Values|common profile values]] |
| Not defined | | Not defined | ||
| Not defined | | Not defined | ||
| Line 119: | Line 117: | ||
Note on ''NAMUR Module Type Package (MTP)'': in the future, basys will map the description for the orchestration of modules that are described via a NAMUR MTP to profiles. | Note on ''NAMUR Module Type Package (MTP)'': in the future, basys will map the description for the orchestration of modules that are described via a NAMUR MTP to profiles. | ||
Therefore an existing profile value like VARIABLES may be used or a new profile value may be necessary. | Therefore an existing profile value like VARIABLES may be used or a new profile value may be necessary. | ||
| − | |||
<!-- TODO Describe (important) profiles values in detail: | <!-- TODO Describe (important) profiles values in detail: | ||
==== SI Profile CMD ==== | ==== SI Profile CMD ==== | ||
| Line 140: | Line 137: | ||
! Value !! Name !! Description !! Possible OCCST values | ! Value !! Name !! Description !! Possible OCCST values | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 0 - 2 || UNKNOWN, NONE, ANY || See [[# | + | | 0 - 2 || UNKNOWN, NONE, ANY || See [[#Profile Values|common profile values]] || Undefined |
|- | |- | ||
| 3 || OCCUPIED || Only one occupier || OCCUPIED | | 3 || OCCUPIED || Only one occupier || OCCUPIED | ||
| Line 159: | Line 156: | ||
! Value !! Name !! Description !! Possible EXMODE values | ! Value !! Name !! Description !! Possible EXMODE values | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 0 - 2 || UNKNOWN, NONE, ANY || See [[# | + | | 0 - 2 || UNKNOWN, NONE, ANY || See [[#Profile Values|common profile values]] || Undefined |
|- | |- | ||
| 3 || MANUAL || Additional manual mode available || AUTO, MANUAL | | 3 || MANUAL || Additional manual mode available || AUTO, MANUAL | ||
| Line 168: | Line 165: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
<!-- DISCUSS | <!-- DISCUSS | ||
add more combinations with SIMULATE mode: SIMAUTO (AUTO + SIM), SIMMANU (AUTO + MANUAL + SIM) and SIMSEMI ... ? | add more combinations with SIMULATE mode: SIMAUTO (AUTO + SIM), SIMMANU (AUTO + MANUAL + SIM) and SIMSEMI ... ? | ||
| Line 184: | Line 180: | ||
! Value !! Name !! Description !! Reference | ! Value !! Name !! Description !! Reference | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 0 - 2 || UNKNOWN, NONE, ANY || See [[# | + | | 0 - 2 || UNKNOWN, NONE, ANY || See [[#Profile Values|common profile values]] || Undefined |
|- | |- | ||
| 3 || PACKML || PackML state machine || ISA TR88.00.02-2008<ref name="PackML">ISA-TR88.00.02-2008 Machine and Unit States: An Implementation Example of ISA-88.</ref> | | 3 || PACKML || PackML state machine || ISA TR88.00.02-2008<ref name="PackML">ISA-TR88.00.02-2008 Machine and Unit States: An Implementation Example of ISA-88.</ref> | ||
| Line 207: | Line 203: | ||
! Value !! Name !! Description | ! Value !! Name !! Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 0 - 2 || UNKNOWN, NONE, ANY || See [[# | + | | 0 - 2 || UNKNOWN, NONE, ANY || See [[#Profile Values|common profile values]] |
|- | |- | ||
| 3 || CONTI || Conti process operation mode with startup and shutdown: BSTATE, STARTUP, SHUTDOWN | | 3 || CONTI || Conti process operation mode with startup and shutdown: BSTATE, STARTUP, SHUTDOWN | ||
| Line 216: | Line 212: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | <!-- TODO | + | <!-- TODO Add EMF metamodell of tests |
== Profile Compliance Testing == | == Profile Compliance Testing == | ||
--> | --> | ||
Revision as of 06:29, 20 January 2020
| Overview | Interface | Implementation |
Contents
Profiles
BaSys control components may be described by the following profiles:
- SI - Service Interface Profile
- Describes how the offered services are structured and how states are represented.
- This profile is special, because it is orthogonal to the other profiles. Hence, every other profile looks a bit different, if a different SI profile is realised in component.
- OC - Occupation Profile
- Describes whether a occuption is necessary.
- Variants may describe whether a occupation with priority or local is possible.
- EM - Execution Modes Profile
- Describes whether different execution modes are possible.
- Variants may describe which modes are possible and how they are called.
- ES - Execution States Profile
- References the used execution states and their transitions.
- May describe variants or subsets of a full execution state state machines.
- OM - Operation Modes Profile
- Describes whether multiple operation modes are available and need to be selcted.
- Variants may describe whether there are specific operation modes, like fallback or startup and shutdown modes.
For example a control component could have the following profile values.
- SI = 5 (OPERATIONS)
- OC = 4 (PRIO)
- EM = 3 (MANUAL)
- ES = 3 (PACKML)
- OM = 4 (MULTI)
The address space of a control component interface in OPC UA is shown in the figure.
Profile Values
All profiles shall be determined with an positiv integer or zero, respectively enums may be implemented. In order to combine profile values and to use them as statements some common values are equal for all profiles, which is presented in the following table.
| Value | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | UNKNOWN | No statement about profile or not determined |
| 1 | NONE | Profile is not realised, used, compliant or implemented |
| 2 | ANY | One ore more profile values, but not specified which ones |
| 3 - n | Profile specific | Specific variants of the profile. |
SI Profile
The control component service interface E1 may be realised in various ways. Basys classifies different realisations via profiles. The service interface profile (SI) describes how a control component can be affected by the means of orchestration and how the resulting state changes may be observed. Therefore each profile value defines how the activation interaction likewise the writing of variables or invocation of operations is handled. Moreover, a component has aggregated state values for its state machines, which may be represented by one or more variables at different adresses. State change events may be raised if state variable values change. Consequently, the SI profile also defines how to find the addresses or endpoints of its activation and reaction represenations.
The following table presents an overview and small comparision of possible SI profile values. The major profile of the service interface used in basys is OPERATIONS.
| SI value | Name | Usage in Basys | Activation mechanism | Aggregated state represenation | Utiliziation recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 - 2 | UNKNOWN, NONE, ANY | See common profile values | Not defined | Not defined | Probably not a compliant basys control component |
| 3 | VARIABLES | Not used in basys | Multiple (spread) variables are used to activate service operations | Multiple (spread) variables are used to represent the component states | Very generic but needs mapping description. Not standardized browseable. May be mapped to NAMUR MTP |
| 4 | CMD | Used in SMS Demonstrator (RWTH) | A string variable called CMD (command input) with a specific syntax is used to activate service operations | A flat list of variables of all aggregated component states under a containing element (folder) | Process control applications with IEC 61131 |
| 5 | OPERATIONS | Used in SMS and common Demonstrator (~All partners) | A flat list of operations of all offered services under a containing element (folder) | A flat list of variables of all aggregated component states under a containing element (folder) | Advanced components or as additional interface |
| 6 | SERVICES | Not used, upcomming in BaSys 4.2 | Operations are grouped under service elements | State variables are grouped under service elements | Advanced and modular components |
Note on NAMUR Module Type Package (MTP): in the future, basys will map the description for the orchestration of modules that are described via a NAMUR MTP to profiles. Therefore an existing profile value like VARIABLES may be used or a new profile value may be necessary.
OC Profile
The occupation profile describes, whether a control component can be occupied. This is important for an orchestrator, as it has to be checked, whether the component is free and it has to be occupied before operation. Further more, the occupation profile determins, whether it is possible to occupy the component with a higher priority, for example by an operator or maintenance person. An OC profile value of two (ANY) or higher requries the component to have an OCCUPIER variable to determine who occupies the component. If the OC profile value is four (PRIO) or higher, the OCCST variable is needed to differentiate occupation states.
| Value | Name | Description | Possible OCCST values |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 - 2 | UNKNOWN, NONE, ANY | See common profile values | Undefined |
| 3 | OCCUPIED | Only one occupier | OCCUPIED |
| 4 | PRIO | Priority possible | OCCUPIED, PRIO |
| 5 | LOCAL | Local overwrite | OCCUPIED, PRIO, LOCAL |
EM Profile
The execution mode profile describes which execution modes are available. A component is assumed to be in AUTO like mode at all time, if the ES value is NONE. An ES value of three (MANUAL) or higher demands a EXMODE variable to determine the mode.
| Value | Name | Description | Possible EXMODE values |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 - 2 | UNKNOWN, NONE, ANY | See common profile values | Undefined |
| 3 | MANUAL | Additional manual mode available | AUTO, MANUAL |
| 4 | SEMIAUTO | Additional semiautomatic mode available | AUTO, SEMIAUTO, MANUAL |
| 5 | SIMULATE | Additional simulation mode available | AUTO, SEMIAUTO, MANUAL, SIMULATE |
ES Profile
The execution state profile defines which execution state machine is used by a reference to common standards. BaSys recommends the use of the PACKML profile as it is possible to map the other state machines to it. [1] The EXST variable has to be present, if an ES value of two (ANY) or higher is given. A control component with ES profile value one (NONE) is assumed to be in the EXECUTE state at all time and hence it can not be halted, suspended, stopped or aborted.
| Value | Name | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 - 2 | UNKNOWN, NONE, ANY | See common profile values | Undefined |
| 3 | PACKML | PackML state machine | ISA TR88.00.02-2008[2] |
| 4 | ISA88 | ISA88 state machine | ANSI/ISA-88.00.01-2010[3] |
| 5 | MTP | MTP state machine | MTP Part 4[4] |
| 6 | OPCUA | OPC UA program state machine | OPC UA Part 10[5] |
| 7 | BASYS | Subset of PackML (Start, Stop, Reset) | PackML without held, suspended, aborted and corresponding active states. |
OM Profile
The operation mode profile defines whether different operation modes are selectable. A control component with an OM value of two or higher has to represent the current operation mode via OPMODE state variable. The OM value NONE yields to a control component, that has no operation modes to select and is therefore assumed to be in BSTATE (basic state) at all time.
| Value | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 - 2 | UNKNOWN, NONE, ANY | See common profile values |
| 3 | CONTI | Conti process operation mode with startup and shutdown: BSTATE, STARTUP, SHUTDOWN |
| 4 | MULTI | Multiple, application specific modes available. |
| 5 | PARALLEL | Parallel executable operation modes with own execution states. See components with concurrent behavior. |
References
- ↑ Wagner, C., Grothoff, J., Epple, U., Grüner, S., Wenger, M., & Zoitl, A. (2018). Ein Beitrag zu einem einheitlichen Engineering für Laufzeitumgebungen, 19. Leitkongress der Mess- und Automatisierungs-technik, Baden-Baden.
- ↑ ISA-TR88.00.02-2008 Machine and Unit States: An Implementation Example of ISA-88.
- ↑ ISA-S88 Part 1 – Batch Control Models and Terminology (IEC 61512-1)
- ↑ VDI/VDE/NAMUR 2658 Part 4 - Modelling of module services
- ↑ IEC 62541 Part 10 – Programs
| BaSyx project links: Project BaSyx main wiki page | What is BaSyx? | BaSyx Developer Documentation |