Notice: This Wiki is now read only and edits are no longer possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Difference between revisions of "EMIWG/MADKQuickStartUseCasesDiscussion"
| Line 165: | Line 165: | ||
===SDK Provider Use Cases=== | ===SDK Provider Use Cases=== | ||
| − | Figure below presents the main use cases diagram in the perspective of the Mobile Application Developer. | + | Figure below presents the main use cases diagram in the perspective of the Mobile Application Developer. Those use case are more high level tasks that need to be performed by the SDK Provider team in order to be integrated into MADK distribution. Since that, the use cases are related to how to implement the extensions and setup the server. This is still a high level description that need to be later detailed. |
| + | |||
[[Image:Usecases_sdk.png]] | [[Image:Usecases_sdk.png]] | ||
| − | |||
* '''[UC001]: Implements SDK Extensions:''' | * '''[UC001]: Implements SDK Extensions:''' | ||
Revision as of 17:17, 9 February 2009
Contents
Objective
The objective of thsi document is to describe all concepts and use cases that are related to MADK Quick Install feature. Below there is a list of all actors, components and use cases related to it. There are two different perspectives proposed. The first one is the mobile application developer perspective that will use MADK to download SDKs and develop mobile applications. The second perspective is from the SDK provider that will need to setup their environment to enable MADK to find / download their SDKs.
Definitions
- MADK: Mobile Application Development Kit. It is an eclipse distribution that enables mobile application development. initially this distribution will include the following eclipse projects: eclipse platform + JDT + MTj + Mylyn + ECF + MADK Extensions;
- SDK Provider: The SDK provider is the entity that develops and provide a Mobile SDK that is user by mobile application developer to write their applications;
- MADK Extensions: MADK Extension provide MADK specific features that are used by mobile developers. Initially there will be only one main extension: the QuickInstall feature. This feature is broken into two components: QuickInstall view and QuickInstall touchpoint;
- MADK QuickInstall view: this view presents connects to MADK server and SDK Providers server to get s list of all SDKs available. Those SDKs are presented to the mobile developer that can download/install, get more information etc.;
- MADK QuickInstall touchpoint: Quickinstall touchpoint is responsible to install each new SDK that is downloaded. This component is distributed with MADK package and each SDK metada must refer it as the touchpoint of the SDK ;
- MADK SDK Discovery Extension Point: This extension point is used by the SDK providers register their SDKs and during the install / remove process. The extension point initially will required
- ID: extension ID
- MADKInstall: class that will implements an org.eclipse.mtj.ISDK. The following methods need to be implemented
- void install () -> called by MADK QuickInstall touchpoint to install the SDK
- void uninstall () -> called by MADK QuickInstall touchpoint to remove the SDK
- IDevice[] getDevices() -> called by MADK QuickInstall touchpoint after the install process to register all devices provided by this SDK. This method is also called everytime that MADK is started to make sure that all Device are still the same
- MADK Server: This server has a reference to all SDKs provider servers. When MADK Quickinstall view connects to thsi server it will query all registered SDK Providers URL for new/updated SDKs;
- SDK Provider Server: Each SDK provider needs to setup it own download server. This server is a usual p2 server that has the following format
- content.xml -> server metadata - artifacts.xml -> server artifacts - binary/ -> NA on SDK Provider server - plugin/ -> SDK Provider plugins - feature/ -> SDK Provider features
- SDK Metadata: describe all SDKs available. It is generated during a P2 metadata generation process (seeGenerating P2 Metadata)
- SDK Provider Extensions: The provider extensions is an implementation of MADK SDK Discovery Extension Point. This implementation needs to be deployed with the SDK Package
- SDK Installer: The SDK installer it self is dependent on each SDK. it can a zip file that is unzipped by the SDK Provider Extensions or a windows installer (executable file) that is executed during the install process by the SDK Provider Extensions;
- SDK Packing format: The packing format describe what needs to be placed on the SDK Provider Server in order that MADK can find and install the SDKs. Below is an example of how 3 SDKs can be packed:
- content.xml -> server metadata. must have as touchpoint MADK QuickInstall touchpoint
- artifacts.xml -> server artifacts
- plugin/
- com.sdkprovider.javame.sdk1_1.0.0.jar
- META-INF/Manifest.mf -> manifest with the SDK version and provider
- installer/sdkprovider_javame_sdk1.exe -> -> SDK installer in a format the SDKInstaller class can understand
- com/sdkprovider/javame/sdk1/SDK1Installer.class -> SDK installer that is called during the install / uninstall process
- plugin.xml -> describe the MADK Install extension point implementation
- com.sdkprovider.javame.sdk2_1.0.0.jar
- META-INF/Manifest.mf -> manifest with the SDK version and provider
- installer/sdkprovider_javame_sdk2.zip -> -> SDK installer in a format the SDKInstaller class can understand
- com/sdkprovider/javame/sdk1/SDK1Installer.class -> SDK installer that is called during the install / uninstall process
- plugin.xml -> describe the MADK Install extension point implementation
- feature/ -> SDK Provider features
- com.sdkprovider.javame.sdk1_1.0.0.jar
- META-INF/Manifest.mf -> feature manifest
- feature.xml -> describe the SDK with its EULA, version, provider and get more info URL
- com.sdkprovider.javame.sdk2_1.0.0.jar
- META-INF/Manifest.mf -> feature manifest
- feature.xml -> describe the SDK with its EULA, version, provider and get more info URL
Actors
- Mobile Application Developer: MADK final user that downloads MADK distribution, download and install new SDKs and develop mobile applications;
- SDK Provider Developer: SDK provider develper that needs to implement the extensions and pack the SDK
Components
- MADK:QuickInstall View: main MADK view that is used to find / install SDKs
- MADK:QuickInstall Touchpoint: p2 touchpoint that installs the SDKs. each SDK must refer this touchpoint
- MADK:MADK Server: ths server is hosted inside Eclipse foundation infra-structure and it has a reference to all SDK Providers URL.
- SDK:SDK Provider Server: Each SDK provider needs to setup its own download server with its SDKs. This is necessary since Eclipse servers can only host EPL content and each SDK will probably have non-EPL content.
- SDK:SDK Extensions: SDK extension are called by MADK:QuickInstall Touchpoint during the install process to install the SDK.
- Eclipse:Eclipse P2: P2 is the basic eclipse component that is used as a base during the download / install process.
Use Cases
Use cases are broken into two groups according to the use case perspective. The first group list all use cases that are related to the mobile application developer actor. On the other hand, the second group focus on the SDK Provider Developer perspective.
MADK Use Cases
Figure below presents the main use cases diagram in the perspective of the Mobile Application Developer.
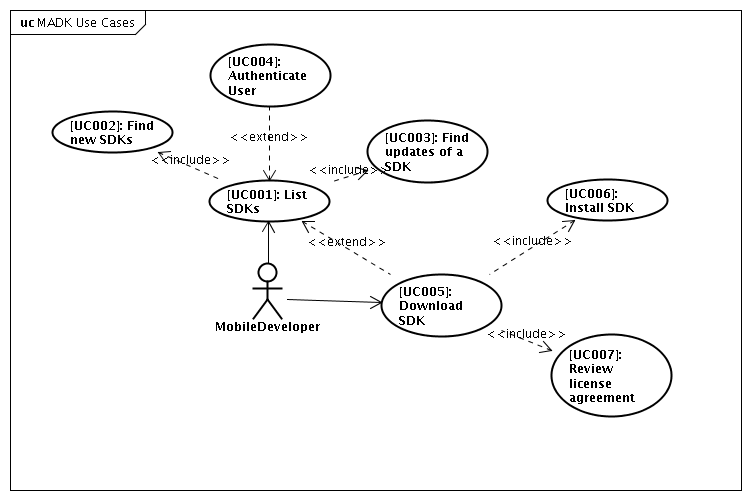
- [UC001]: List SDKs:
This is the first use case tht the mobile application developer can execute. It presents a list of all SDKs that available grouped by provider. Each SDK can be in 3 different states:
- New: SDK is not installed in this current MADK distribution. This might be a new SDK or an SDK that was installed but removed on the past;
- Installed: SDK is installed on current MADK distribution;
- Updates: SDK is installed and there are updates to this SDK.
Main Flow: 1. User opens the quickinstall view 2. Quickinstall view connects to MADK server to list all available SDK Providers repositories 3. Quickinstall view connects to each SDK Provider Servers to list all availables SDKs (may execute secondary flow 1) 4. Quickinstall view presents a list of all available SDK grouped by provider 5. Execute UC002 (may execute secondary flow 2) Secondary Flow: 1. SDK Provider Server requies an authentication. User should enter the User Name / URL 2. If the SDK is already installed, execute UC003
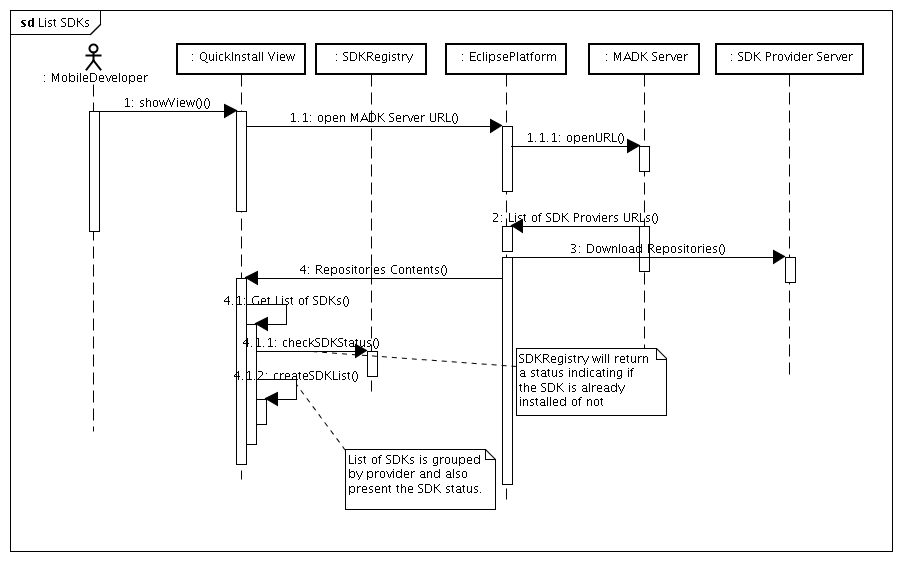
Below image presents a sequence diagram that of the List use case. This is just a high level diagram that does not intent to have the actual classes/methods that might be used on a real implementation.
Below image give a idea of how the List SDKs UI might be. This is just an initial proposal that can be changed in the future.

- [UC002]: Find new SDKs:
This use case is included on UC001. It handles the scenario of a SDK that is not yet installed or that was installed and removed in the past. The SDKs in this scenario will be listed as NEW and the user will be able to download and install each of them. ([gep] should we support multiple simultaneous SDK downloads?)
Main Flow: 1. New SDKs are presented on the highlights on the SDKs list 2. New SDKs are listed with a "NEW" indication. The following information are presented on each New SDK - Name - Version - Brief Description - URL to get more information
- [UC003]: Find updates of a SDK:
This use case is similar to UC002. The main difference is that the SDKs in this scenario are already installed and there is an updated version of it. This SDK only make sense if there is some kinbd of internal solution on the SDK itself to update it. For example, if the SDK is provided just as a zip file, an updated version of it, might just unzip the updated on top of the previous installation.
Main Flow: 1. Based on the currently installed Features, MADK checks which SDKs are already installed 2. After, it checks if there is an update for this SDK. 3. If there is not, the SDK is highlighted with a "INSTALLED" indication 4. If there is, the SDK is highlighted with a "UPDATEAvailable" indication 5. New SDKs are listed with a "NEW" indication. The following information are presented on each New SDK - Name - Version - Brief Description - URL to get more information
- [UC004]: Authenticate User:
This might be necessary if the SDK is not directly available on the internet. In this situation, the user needs to enter a user name / password that will be validated at the SDK Provider Server. Based on the, the user might get access or not to the server content.
Main Flow: 1. Quickinstall view will present a dilog box with: - title of the repository that it is trying to access - a login / password field - ok / cancel button 2. The user presses OK (may execute secondary flow 1) Secondary Flow: 1. If the user presses CANCEL, that repository will not be accessible and its SDKs will not be listed
- [UC005]: Download SDK
The download process will reuse all P2 download protocol.
Main Flow: 1. User selects one specific SDK to download 2. Quickview will check if all components required by this SDK are available (may execute secondary flow 1) 3. All components are available, UC007 (Review License Agreement) is executed 4. The SDK and SDK extensions are downloaded (may execute secondary flow 2) 5. EclipsePlatform Request Quickinstall touchpoint to install the SDK 6. Execute UC006 (Install SDK) Secondary flows: 1. All required components are not available: quickinstall view will show the user the list of componnts that also need to be downloaded. The user will need to download them to continue 2. Network error: if there is any network error the install process is aborted
- [UC006]: Install SDK
The main aspect to highlight on this use case is that, the Quickinstall touchpoint shall be used to install the SDK. This touchpoint will call the SDKInstaller implementation that should be responsible to install the SDK itself. This will give more flexibility to each SDK provider to define their SDK package format.
Main flow: 1. Quickinstall touchpoint calls the SDK installer (may execute secondary flow 1) 2. Quickinstall touchpoint installs all SDK extensions (may execute secondary flow 2) 3. SDK state is changed to "INSTALLED" Secondary flow: 1. Installer error: if there is an error during the installer execution, the install process is aborted 2. quickinstall touchpoint not found: if quickinstall touchpoint is not available on MADK, the install process is be aborted
- [UC007]: Review license agreement
This is part of the usual P2 download process and the idea of this use case is to keep the same behavior.
Main flow: 1. Feature EULA is presented to the user 2. The user accepts the EULA (may execute secondary flow 1) Secondary flow: 1. User does not accept EULA: the install process is aborted
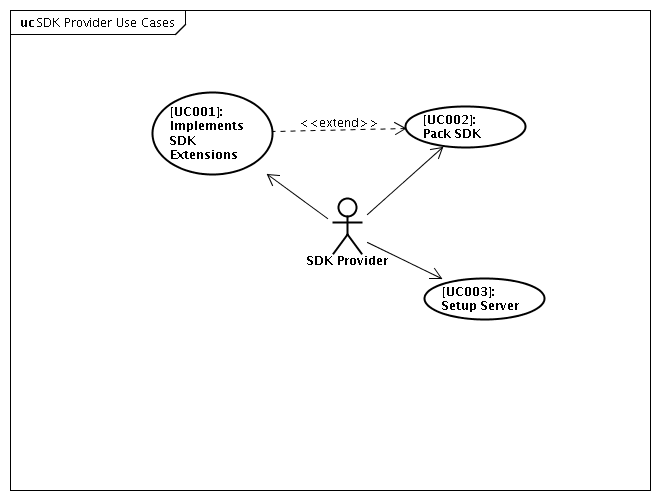
SDK Provider Use Cases
Figure below presents the main use cases diagram in the perspective of the Mobile Application Developer. Those use case are more high level tasks that need to be performed by the SDK Provider team in order to be integrated into MADK distribution. Since that, the use cases are related to how to implement the extensions and setup the server. This is still a high level description that need to be later detailed.
- [UC001]: Implements SDK Extensions:
The extension is necessary, since is describes to install the SDK.
Main flow: 1. SDK Provider should implement the extension point that describe how to install / uninstall / configure the SDK 2. The SDK extension must be packed with the SDK it self
- [UC002]: Pack SDK:
The SDK will be packed in a way that the extension can install it.
Main flow: 1. SDK Provider shall pack the SDK in a single feature and a single plugin. The plugin must include - SDK Extensions - SDK Installer 2. The SDK must be build using standard PDE build system
- [UC003]: Setup Server:
The SDK Provider Server is a usual P2 server.
Main flow: 1. SDK provider setup its p2 server according to p2 design 2. SDK provider might setup different permissions level to the repository 3. SDK provider ask MADK Server to add its repository URL to the list of available SDKs