Notice: this Wiki will be going read only early in 2024 and edits will no longer be possible. Please see: https://gitlab.eclipse.org/eclipsefdn/helpdesk/-/wikis/Wiki-shutdown-plan for the plan.
Java18/Examples
Revision as of 04:52, 21 February 2022 by Niraj.modi.in.ibm.com (Talk | contribs)
This is an informal page listing examples of features that are implemented by the Java 18 Support, which can be installed from the Marketplace. You are welcome to try out these examples. If you find bugs, please file a bug after checking for a duplicate entry here
Watch out for additional examples being added soon.
NOTE:
- Sealed Classes is a standard features in Java 18.
- Restore Always-Strict Floating-Point Semantics is a standard features in Java 18.
- Pattern Matching for switch is preview feature in Java 18. They are not enabled by default and can by enabled using --enable-preview.
- In Eclipse, --enable-preview can be enabled from the Preferences. It is implicitly added while launching a java program if the feature has been enabled for the project/workspace.
| Feature / Steps | Expected Result | |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Java/JRE setup with Eclipse | More details can be found on dedicated Java/JRE setup page. | Setting up Java/JRE in Eclipse. |
| Overview of eclipse.ini | More details can be found on dedicated eclipse.ini page. | Specifying the JVM in eclipse.ini |
| Preview Feature: Pattern Matching for switch | ||
| Postive compilation1 (Pattern Matching for switch Example) | Use the following code:
public class X { private static void foo(Object o) { switch (o) { case Integer i -> System.out.println("String:"); case String s -> System.out.println("String: Hello World!"); default -> System.out.println("Object"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { foo("Hello World"); } } |
Code compiles and prints below message: String: Hello World! |
| Positive compilation2 (Pattern Matching for switch Example) | Use the following code:
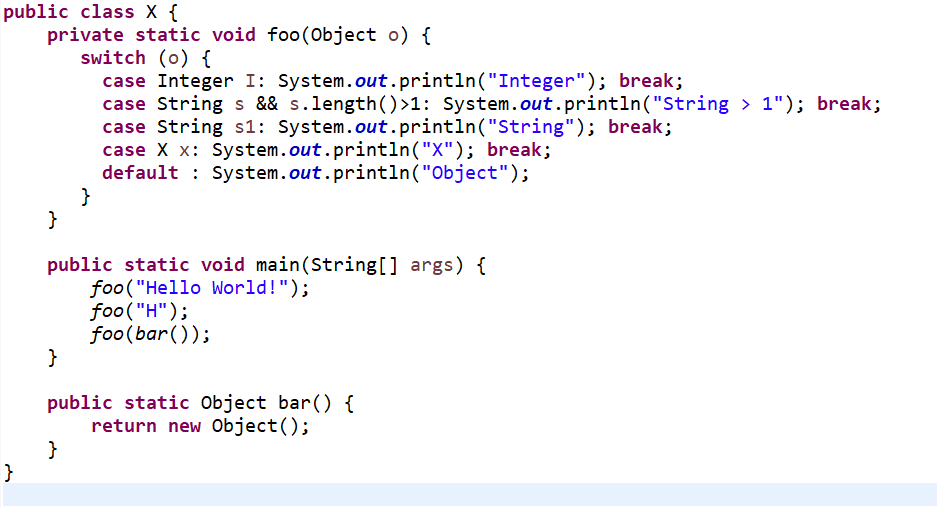
public class X { private static void foo(Object o) { switch (o) { case Integer I: System.out.println("Integer"); break; case String s && s.length()>1: System.out.println("String > 1"); break; case String s1: System.out.println("String"); break; case X x: System.out.println("X"); break; default : System.out.println("Object"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { foo("Hello World!"); foo("H"); foo(bar()); } public static Object bar() { return new Object(); } } |
Code compiles and prints below message: String > 1 |
| Positive compilation3 (Pattern Matching for switch Example) | Use the following code:
public class X { private static void foo(Object o) { switch (o) { case Integer I: System.out.println("Integer"); System.out.println(I); break; case String s && s.length()>1: System.out.println("String s && s.length()>1"); System.out.println(s); break; case String s: System.out.println("String"); System.out.println(s); break; case X x: System.out.println("X"); System.out.println(x); break; default : System.out.println("Object"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { foo("Hello World!"); foo("H"); foo(bar()); } public static Object bar() { return new Object(); } } |
Code compiles and prints below message: String s && s.length()>1 |
| Positive compilation4 (Pattern Matching for switch Example) | Use the following code:
public class X { public static void main(String[] args) { foo(Integer.valueOf(11)); foo(Integer.valueOf(9)); } private static void foo(Object o) { switch (o) { case Integer i && i>10: System.out.println("Greater than 10:" + o); break; case Integer j && j>0: System.out.println("Greater than 0:" + o); break; default: System.out.println("Object" + o); } } } |
Code compiles and prints below message: Greater than 10:11 Greater than 0:9 |
| Positive compilation5 (Pattern Matching for switch Example) | Use the following code:
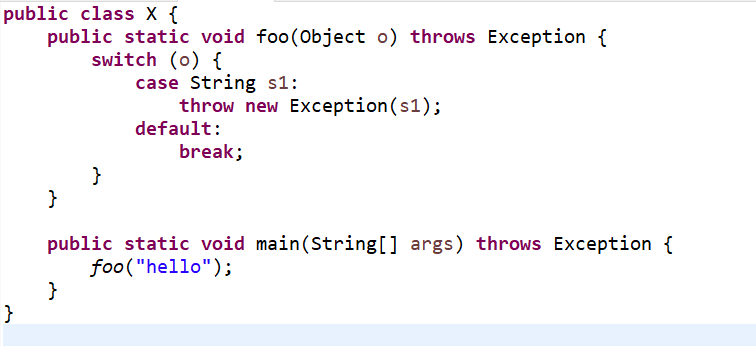
public class X { public static void foo(Object o) throws Exception { switch (o) { case String s1: throw new Exception(s1); default: break; } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { foo("hello"); } } |
Code compiles and prints below exception stack trace message: Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Exception: hello |
| Standard Feature: Restore Always-Strict Floating-Point Semantics | ||
| Positive compilation1 (Restore Always-Strict Floating-Point Semantics Example) | Use the following code:
strictfp public class X { // strictfp applies to all methods in this class } |
Code compiles: strictfp applies to all methods in this class |